
Entering the European market for web design and web application development
To enter the European market for web design and web application development services, you must comply with different laws and regulations. Examples include the GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive. Buyers often have additional requirements. The best way to gain access to different horizontal and vertical market segments is by working with a strategic partner. The strongest competition comes from central and eastern Europe.
Contents of this page
- Which requirements and certifications must web design and web application development meet to be allowed on the European market?
- Through which channels can you get web design and web application development on the European market?
- What competition do you face on the European web design and web application development market?
- What are the prices of web design and web application development on the European market?
1. Which requirements and certifications must web design and web application development meet to be allowed on the European market?
The most important general mandatory requirements for web design and web application development services are the GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive. These are mentioned below, as well as in our study about Entering the European market for software development services.
New legislation is always being drafted. Listing or knowing all the regulations would be impossible, so this chapter just discusses the most common requirements.
What are mandatory requirements?
The main mandatory requirements for your services are stated in the GDPR, ePrivacy Directive, and the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
As a web developer you have to comply with the European Union (EU) General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This makes processes more complex. You need to implement clear consent mechanisms, data minimisation strategies, robust data storage and security measures. You also need to have mechanisms in place to facilitate user rights such as access and erasure of personal data.
Tips:
- You can use the website auditing tool developed by the European Data Protection Board to check whether your website is compliant with the GDPR. The tool is a Free and Open Source Software and can be downloaded from code.europa.eu.
- You can also use free online GDPR compliance checkers such as the Cookiebot CMP, ImmuniWeb or 2GDPR.com.
ePrivacy Directive
The ePrivacy Directive, commonly known as the “cookie law”, contains specific regulations for data protection in the electronic communications sector. For example, it forbids unsolicited commercial electronic messages (“spam”). It contains strict rules on cookies, and contact details may only be published with the subject’s consent. It complements the GDPR.
Read more about this requirement and the upcoming new ePrivacy Regulation in our study about Entering the European market for software development services.
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are a set of technical standards and guidelines developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) to ensure that web content is accessible to people with disabilities. WCAG provides a framework for making web content more visible, operable, understandable and robust for all users, including those with disabilities.
In 2025 the European Accessibility Act will come into effect.
The guidelines are organised into 4 principles, each with specific success criteria:
Visible:
Information and user interface components must be shown in ways that users can understand. This includes giving text descriptions for non-text content like images and videos, making sure content can be adjusted and is clear, and helping users see and hear content more easily.
Operable:
All users should be able to work with user interface components and navigation, including those with disabilities. Firstly, it should be possible to navigate content using a keyboard. Users should also have sufficient time to interact with content. Finally, you should ensure that users can easily pause, stop, or hide moving, blinking or scrolling content.
Understandable:
Content and navigation must be understandable to users, including those with cognitive or learning disabilities. This includes making text content readable and understandable, ensuring predictable website behaviour, and providing clear and consistent navigation.
Robust:
Content must be robust enough to work across different browsers, devices, and assistive technologies. This involves using semantic markup, ensuring compatibility with assistive technologies, and avoiding reliance on specific technologies that may not be supported by all users.
WCAG is organised into 3 levels of conformance: A (minimum), AA (mid-range), and AAA (highest). Each success criterion is assigned a level of conformance based on its impact on accessibility. Level AA is the standard level recommended for most web content.
Compliance with WCAG is essential for ensuring that websites and digital content are accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. Following these guidelines not only benefits people with disabilities but also improves usability and user experience for all users.
Tip:
- Find out how accessible your website is by using this web accessibility evaluation tools list.
What are additional requirements and certifications buyers often have?
Additional requirements concern corporate social responsibility (CSR) and project management.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Having CSR-related certifications gives you a competitive advantage. Most European buyers of web design and web application development services will either demand, or highly value, certification relating to CSR. You can read about why CSR is important and how you can implement it in the 2 documents: 'Tips to go green' and 'Tips to become a socially responsible supplier'.
Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive and Forced Labour Regulation
Important Green Deal legislation has been approved in 2024. It includes the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) and the Forced Labour Regulation. EU member states will have 2 years to implement the regulations and administrative procedures to comply with these rules. It requires larger companies (exact number to be found on the website of the European Commission) to identify and – where necessary – prevent, end, or reduce any negative impacts of their activities on human rights and the environment. Both in the company’s own operations and in its value chains. This means that the new rules may apply to you indirectly via your buyers.
In 2024, the EU adopted a new Forced Labour Regulation. Complementing the CSDDD, this regulation bans products from the EU market when they are made with forced labour.
These laws are relatively new and might not apply to you yet, however you should familiarise yourself with them and be prepared for their rollout.
Tips:
- Read more about the CSDDD.
- For details on the Forced Labour Regulation, check out the questions and answers and the factsheet.
- Stay up to date on the proposed rollout of the new CSDDD and the Forced Labour Regulation.
Web analytics tools
Many organisations use web analytics tools to track user behaviour. Web analytics tools are software that help track and analyse how people use a website. These tools can show how many people visit a website, what pages they look at, how long they stay, and if they complete certain actions like filling out a form or making a purchase. This data helps businesses understand what is working well on their website and what needs improvement.
By looking at the data from these tools, you can see how users interact with a website. This information helps you create websites that are easier to use and more engaging. For example, if you see that users often leave a website quickly, you can change the design to make it more appealing or easier to navigate.
Some popular web analytics tools are Google Analytics, Matomo, Umami, and Adobe Analytics. Google Analytics provides detailed reports on website traffic and user behaviour. Matomo Analytics is an open-source tool that provides detailed reports on website traffic and user behaviour while respecting user privacy. Umami is another open-source tool that offers simple and privacy-focused analytics. Adobe Analytics is a good option for advanced data analysis and works well with other Adobe products.
European buyers might ask for this feature to be embedded in their website. Some European countries such as Austria, France and Italy have banned the use of Google Analytics on websites. They did this because Google collects a lot of data on user behaviour and uses it for its own needs. It is likely that other European countries will follow.
Project management
European buyers increasingly demand providers to work with a project management tool. A popular example is Agile. It is based on the Agile Manifesto, which discusses the ability to respond to change. It focuses on how people work together, letting solutions evolve through collaboration between self-organising and cross-functional teams.
Agile software development advocates adaptive planning, visualisation, evolutionary development, early delivery and continual improvement. Scrum is the most widely used Agile framework.
What are the requirements for niche markets?
On the European market for web design and web application development, requirements vary per industry, segment, technology and even country. Different industry-specific standards, rules, and regulations exist for education, healthcare and so on.
Country
We recommend checking the specific rules for your European target market.
You can find an overview of country-specific measures affecting trade, which are different from international standards, on the ePing website (an initiative of the WTO, ITC and UN). This website also lists contact details for country agents appointed by the World Trade Organisation (WTO). You can subscribe to receive ‘e-Ping alerts’ that are relevant for your product or service.
Industry
Different industries set different requirements. In healthcare, for example, Health Level 7 (HL7) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) are important. In the automotive industry, MISRA and AUTOSAR are the 2 main coding standards used, but ISO 26262 and ISO 15504 are also applicable.
Example MDaaS
MDaas is a Nigerian company that develops web applications for the healthcare industry. Their healthcare products and services make it easier for Africans to access and afford quality care. They provide a range of services including diagnostic centres and hybrid health management platforms.
Technology
Relevant European requirements for specific technology are the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act and cyber security for consumer internet of things requirements.
European buyers often require knowledge of and experience in specific technology. Examples of technologies used in web design and web application development are:
- HyperText Markup Language (HTML): The backbone of any web page, used for structuring content;
- Cascading Style Sheets (CSS): Used for styling HTML elements and determining the layout of web pages;
- JavaScript: The primary language for adding interactivity and dynamic behaviours to web pages;
- Frontend Frameworks (like React, Angular, Vue.js): These frameworks simplify the process of building complex user interfaces and managing state in web applications;
- Backend Frameworks (like Node.js, Django, Ruby on Rails): Provide tools and libraries for building server-side logic and handling requests from clients;
- Database Management Systems (like MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL): Used for storing and retrieving data in web applications;
- Version Control Systems (like Git): Essential for managing code changes, collaborating with team members, and maintaining codebases;
- Security Practices (like HTTPS, Authentication, Authorisation): Ensuring the security of web applications by protecting against common vulnerabilities like cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection;
- Containerisation and Orchestration (Like Docker or Kubernetes): Technologies for packaging and deploying web applications in isolated environments, making them easier to manage and scale.
Tips:
- Closely follow the European Union’s development of laws and regulations relating to the technology that is used in web design and web application development services.
- Learn from your clients and monitor potential clients to see what requirements they find important. Together you can work on certifications or social goals.
- Check which sector-specific standards or codes are available for your specific product (for example, by asking your sector association or your buyer) and to what extent your buyer wants you to implement them.
- Read about specific security risks for the product or service you are offering. For example, look at this document that provides the top 10 security risks for web applications.
2. Through which channels can you get web design and web application development on the European market?
The most realistic way to enter the European marked is by working with a strategic partner. For web design and SEO services, online platforms can also be promising.
How is the end market segmented?
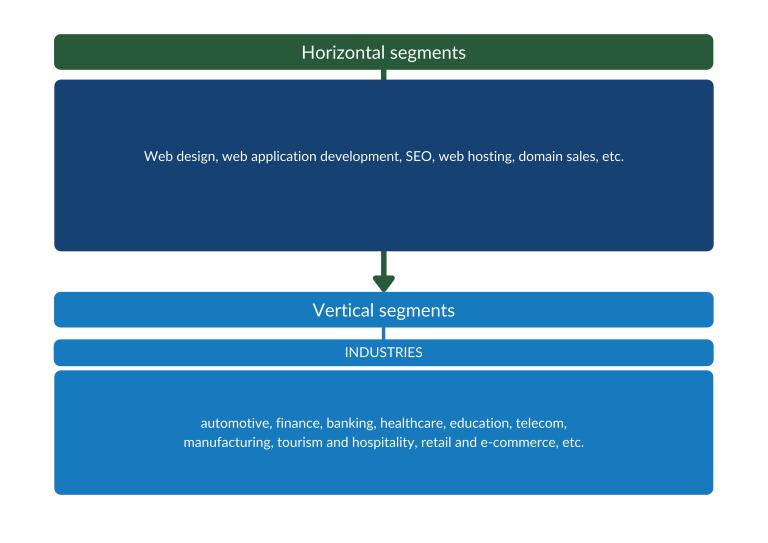
The European market for web design and web application development can be divided into horizontal and vertical market segments. You can tap into these segments through several different market channels.
Figure 1: Horizontal and vertical market segments with opportunities for service providers
Source: Globally Cool
Segmentation can be done by horizontal or vertical market. If your service is a relative commodity (which many web design and web application development services are), focus on a niche segment or industry. There are many ways to do that, for example:
- Specialise in emerging technologies. This could include expertise in responsive design, mobile optimisation, progressive web apps, voice user interfaces or immersive technology like virtual reality or augmented reality.
- Specialise in user experience (UX). Focus on creating websites that prioritise usability, accessibility, and user satisfaction. To do that, you can conduct user research, usability testing, and user mapping to optimise the overall user experience.
- Become an expert in accessibility and inclusive design. Ensure your websites are compliant with accessibility standards such as WCAG and prioritise designing with all users in mind, including those with disabilities. If you are good at this, you can offer potential buyers audits and remediation services on this subject.
- Focus on visual branding and identity as a part of your web design or web application development services. Emphasise how good you are at helping buyers establish a cohesive brand identity from their logo to their website via typography, colour palette and other visual assets.
- Offer cross-platform development. Emphasise the possibilities it can offer your buyers to help reach a wider audience across different devices and platforms. You can offer expertise in developing responsive, adaptive and scalable web applications that perform well on desktops, tablets and mobile devices.
Greenbox Designs is a good example of a web design and web application development company that knowns how to combine a successful business with sustainability standards. Located in Cape Town, South Africa, Greenbox Designs is known for its commitment to sustainability. The company focuses on building long-term, sustainable relationships with its clients. It also emphasises using clean, intelligent design to create websites that are both beautiful and easy to use. Greenbox Designs integrates sustainable practices into their projects, aiming to minimise environmental impact while providing high-quality digital solutions.
Through which channels do web design and web application development services end up on the end market?
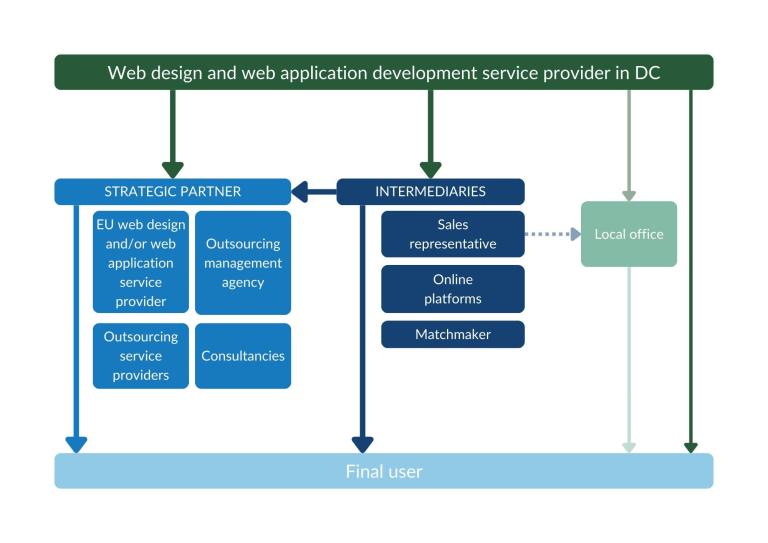
There are various channels through which web design and web application development services end up on the end market, see figure 2. This trade structure is very similar in every European country. Working with a strategic partner is your most realistic market entry channel.
Figure 2: Trade structure for outsourcing web design and web application services in de European market
Source: Globally Cool
Strategic partner
Working with a strategic partner is your most realistic market entry channel. They could be Independent Software Vendors (ISVs), outsourcing management agencies, outsourcing service providers or consultancies.
A provider that is similar to your company would be most suitable. Ideally, this company should design, develop, market, sell and maintain its own web design and/or web application development similar to yours.
The relationship between a strategic partner and a subcontracted supplier (you) is generally characterised by:
- Trust;
- Dependence on each other;
- A structured relationship (functions, tasks, communication, and procedures);
- Potentially limited marketing visibility and market access opportunities for the subcontracted supplier;
- No intellectual property (IP) rights, or a loss of IP rights for the subcontracted supplier;
- When there is no guaranteed amount of work, work orders are on an if/when-needed basis.
Please note that when you work with a strategic partner, they communicate with the final user of the product or software you are developing. You are merely a subcontractor. The ITO service provider (you) will not appear in marketing communications of the strategic partner. You will be referred to as ‘delivery centre’.
You can find a strategic partner either directly or by working with an intermediary. Because many European companies prefer to deal with a local contact person, an intermediary is a good option.
Tips:
- Attend leading (online) European trade fairs, to meet competitors and potential customers. Do your homework and select events that fit your profile. Make a list of relevant events using trade event directories, such as 10Times and UK Exhibitions and update it regularly.
- Use IT industry associations to find potential customers, such as Bitkom in Germany, NLdigital in the Netherlands and techUK and BIMA in the United Kingdom. Or look for more options on Digital Europe. If you specialise in a particular industry, you can also use associations for that niche, such as the Association of British HealthTech Industries.
- Use outsourcing associations to find potential customers, such as the Global Sourcing Association, the German Outsourcing Association and Sourcing Nederland.
Intermediary
You can work with an intermediary to find a buyer. This is different from working with a strategic partner where the final user of your software will most likely not know your name, because you are the subcontractor. However, you can use an intermediary to find a strategic partner. Examples of intermediaries are sales representatives, online platforms and matchmakers.
Sales representatives
These are more involved in the sales process than matchmakers. When working with a sales representative remember that:
- The sales representative contacts prospects for you;
- The sales representative also makes the sales and sometimes manages projects to a certain degree;
- You pay a retainer and success fee or a fixed monthly fee;
- The sales representative can have multiple clients or work exclusively for you.
A good sales representative has a large, relevant network, so they do not make cold calls. Their success fee is often a percentage of the arranged meetings, developed leads or sold projects. The exact rate will depend on several factors but can be up to 20% of the project value. Hiring a sales representative will increase your expenses, but you will be free to focus on your core business and search for other markets yourself.
Online platforms
Electronic marketplaces are a cheap marketing tool that may make direct sales easier. They can also help you find companies to work for. Possibly as an independent consultant (someone from your team), or as a subcontracting team. These platforms used to focus on freelancers but are increasingly suitable for SMEs. Online platforms are more realistic for companies that offer web design or SEO services, not so much for web application developers.
Matchmaker
A matchmaker is a person or company with many relevant contacts in a specific market segment or industry. As an intermediary, they can help you to get in contact with relevant people. They are, however, not going to make cold calls or send cold emails. You have to properly inform your matchmaker about your company. They speak with many potential customers and often create long lists of potential outsourcing providers. The more information they have on your company and the better they understand your capabilities, the more they can spread the word about you.
If you work with a matchmaker:
- The matchmaker makes appointments with prospects for you;
- The presentation and sales process remains in your own hands;
- You pay a retainer and a success fee;
- The matchmaker usually has multiple clients;
- You need to set clear expectations and objectives (and exit criteria) to measure their performance.
A retainer and success fee can be expensive. While the success fee depends on what the intermediary has delivered, you must pay the retainer (usually a fixed monthly payment) regardless of their performance. Together, they should provide a strong motivation for the intermediary to deliver: the retainer should be high enough to cover some of the costs, but low enough to encourage delivery. A properly drafted contract by a lawyer is a must!
You also need to determine an exit strategy in the contract, with a clearly defined period after which the contract can be terminated without any further consequences. This period is usually not longer than 3 or 4 months, after which the contract will be evaluated and can be terminated or extended. For this period, there should be clearly defined delivery expectations and targets for the consultant/matchmaker (such as the number of relevant contacts, meetings and leads). You could also negotiate a trial period.
Tips:
- Be cautious if intermediaries only ask a success fee for their work, because either they are excellent at their job, or they are desperate and may not (be able to) deliver. You should also be cautious if intermediaries want to work for you part-time besides their regular job, because they are often so busy that they do not deliver.
- When contracting an intermediary, involve a good lawyer who knows the applicable law of the country where the intermediary resides and has experience with this type of contracting. Pay special attention to exit clauses, success criteria, deliverables and payments.
- Try to avoid limitations to your marketing coverage and activities in your contracts.
- While your uncle in Germany may offer a convenient option, we advise you to consider a professional intermediary who has specific expertise and experience in the local market to better support your company's needs.
Local office
There are advantages to opening a local office in your European target market. You can also choose to open an office in one of Europe’s nearshoring destinations as this is generally cheaper.
A local presence makes it easier to build long-term relationships with customers through personal contact. It also increases your credibility, builds trust and allows you to keep complete control over your marketing and sales activities. However, this is very difficult in practice, as it requires a lot of experience and large investments. Most companies in developing countries are simply too small and do not have the financial strength or enough verified market opportunities for this.
Tips:
- Be aware that establishing a local sales office is very costly and you need a strong financial position.
- Consider establishing your own office if you have already established a client base in the target market, or if you have a well-founded idea of the demand for your services/products. If you decide to establish an office, involve your sales/marketing representative.
- Look for alternatives to lower your costs, such as business incubators or government incentives to bring your business to a particular country/region.
Direct sales
You can also try to sell your services directly to European end users. Many European companies are looking for cost reduction and delivery capacity, which developing countries can often provide. This is one of your unique selling points (or at least a competitive selling point). However, you should be aware that these end users might not have qualified IT staff to work with.
Direct sales require experience in the European market and are most suitable for relatively large providers that want to target large European end users. Your best bet is to focus on a small, underserved niche market. For most suppliers from developing countries, however, it is very challenging to sell web application development services directly. Providers of web design and/or SEO services have more chance of success through this channel.
Sometimes, web designers and SEO specialists work together to make a direct sales offer. Having one or more existing customers in Europe will help, as references are a must for direct sales.
Tips:
- Combine offline and online promotion channels to develop as many contacts as possible. This maximises your chances of finding suitable partners/customers. Use social media platforms as a marketing tool. LinkedIn can be particularly useful for making initial contacts and conducting market research.
- Have a professional, high-quality company website. This way you can present full, accurate and up-to-date details of your services at a low cost. Make it compatible with mobile devices and invest in Search Engine Marketing and Optimisation (SEM/SEO), so potential customers can easily find you online.
- Look for potential leads on online platforms like Appfutura and Talent Alpha (specialised in SMEs), or UpWork, Freelancer, Fiverr, ITeXchange, Clutch, Proxify and pliXos. Or sign up for platforms that have their roots in Africa like Terawork or Gebeya, or platforms that operate more on the Asian market like Wellfound or TechHub Asia.
- More general information on how to find buyers in Europe for the ITO and BPO sector can be found in the study 9 tips for finding buyers on the European outsourcing market.
What is the most interesting channel for you?
Your most promising channel for entering the European market is finding a strategic partner. Other ways include working with intermediaries, followed by direct approach and online platforms. The last one is opening your own office. It must be noted that for some services, like SEO or web design, good sales opportunities can also be found in online platforms or even directly.
Which channel is right for you depends on your type of company, the nature of your service, your target market and the available resources for market entry. Understand that, regardless of the channel you choose, your own marketing and promotion is a vital part of your market entry strategy, for which you are responsible.
3. What competition do you face on the European web design and web application development market?
The market for web design and web application development is highly competitive. European companies generally prefer outsourcing to providers within their own country (also known as home sourcing or just outsourcing). When they do outsource to companies abroad, they usually prefer nearshore locations, because of proximity, language, cultural similarities, and the minimal time difference.
Which countries are you competing with?
The strongest competing countries that you will face on the European market are India, Poland, Hungary and Egypt. These countries also score high on the Global Services Location Index (GSLI), which ranks the competitiveness of ITO/BPO destinations based on financial attractiveness, people skills and availability, business environment and digital resonance.
Table 1: Global Services Location Index
| Financial attractiveness (35%) | People skills and availability (25%) | Business environment (25%) | Digital resonance (15%) |
| Compensation costs | ITO/BPO experience and skills | Country environment | Digital skills |
| Infrastructure costs | Labour force availability | Country infrastructure | Legal and cybersecurity |
| Tax and regulatory costs | Educational skills | Cultural adaptability | Corporate activity |
| Language skills | Security of IP | Outputs |
Source: GSLI
Source: Kearney
India: Low-cost destination, mostly known for bulk projects
India continues to lead the Global Services Location Index (GLSI). This leading position is mainly due to the country’s unique combination of low-cost services and English language skills. This attractive profile makes India a particularly strong competitor on the IT outsourcing market.
To stay ahead, India will need to prepare itself for the transition from lower-skilled jobs that may be replaced by robots to more creative and highly-skilled work. This applies to other low-cost countries as well.
India’s reputation as a web design and/or web application development outsourcing destination is fine. It is mainly known for bulk work and standardisation. Most web design and web application development require creativity and a very good understanding of what the client needs. This is generally not India’s strong point.
In addition, India’s language advantage is getting smaller. Many other countries are catching up, while India’s overall language skills have not improved.
European buyers often associate extremely low developer rates in Asian countries with poorer project quality. They assume that cheap service providers must be using less skilled or less experienced service developers, or even that the developers’ working conditions must be poorer.
Central and eastern European (CEE) countries: Strong competition, but also interesting for collaboration
Like many CEE countries, Poland and Hungary are major players in software development, including web design and web application development.
Many CEE countries can offer a combination of a skilled workforce, cost-effectiveness, central European location, cultural compatibility, innovation ecosystem, and government support. This makes them a favourable destination for web design and web application development outsourcing.
Poland saw a large increase in its GSLI ranking from 2019 to 2021. The increase was primarily due to its financial attractiveness and start-up activities. In 2023 it went down a few places (currently 13th) mainly due to other countries performing even better.
Polish people also score very highly on English proficiency, making it relatively easy for European clients to communicate with them. This makes the country a particularly fierce competitor for you.
Hungary is currently number 19 in the GSLI. The country jumped 6 places from 2019 to 2021 and another 18 from 2021 to 2023. Hungary’s strong investments in emerging technologies like IoT and AI- and IT-friendly policies such as financial support have convinced companies to establish R&D centres there.
Bulgaria is another strong competitor in line with Hungary, but also Romania, Serbia and Macedonia. Learn more about CEE countries as ITO destinations by reading their destination guides issued by the German Outsourcing Verband. You can also check out the destination guides of Poland, Romania and Bulgaria.
Besides being strong competition, these countries can also be interesting destinations for finding a strategic partner to become a sub-contractor for.
Egypt: Emerging destination
Egypt is a strongly emerging African destination for offshoring, however its lack of digital focus made it drop 8 places in the GSLI from 2021 to 2023. Its time zone (GMT+2) partly overlaps with western and northern Europe, eliminating the time differences generally associated with offshoring.
The country ranks 23rd in the GSLI, as its considerable investments in infrastructure and cybersecurity are boosting the country’s business environment performance. The New Administrative Capital is designed as a Smart City, and is meant to create an Egyptian Silicon Valley.
The country is home to a large technically-educated workforce that is skilled in English, Arabic, French, German, and other European languages. The hourly developer rates in Egypt are relatively low at €17–€34, which is comparable to the average rates in Asia. Learn more about Egypt as an ITO or BPO destination by reading their destination guide, issued by the German Outsourcing Verband.
Tips:
- Compete on the quality of your services, rather than just on costs.
- Specialise in specific horizontal/vertical markets, emerging technologies and/or niche market segments to avoid competition.
- Visit the websites of IT outsourcing associations and software development associations to get a better understanding of competing countries. Examples are the Central and Eastern European Outsourcing Association (CEEOA), ICT Africa, PITA from Palestine and the Ghana Export Promotion Authority (GEPA).
- Look at the website of the German Outsourcing Verband. They have useful guides about IT destinations, for example about Morocco, Ghana, the Caribbean and Rwanda.
Which companies are you competing with?
Examples of web design and/or web application development companies are:
Netguru
Netguru is a leading software development and design company based in Poland. They offer web development, mobile app development, UX/UI design, and product design services to clients worldwide. Netguru has worked with various start-ups, enterprises and digital agencies across industries such as fintech, healthcare and e-commerce.
For example, they developed a secure and user-friendly mobile banking app for a leading fintech company, providing seamless access to financial services and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
Supercharge
Supercharge is a Hungarian digital product development company specialising in web and mobile app development, UX/UI design, and product strategy. They have a team of experienced developers, designers, and product managers who work with start-ups and Fortune 500 companies to create innovative digital solutions.
One notable project includes developing a responsive and feature-rich e-commerce platform for a fashion retailer, integrating advanced search and filtering functionalities to enhance the shopping experience for users.
Blink 22
Blink 22 is a software development and web application development company that is based in Egypt. They have successfully made use of the trend of providing tailored solutions to meet the needs of their international clients. Their website also clearly shows they offer user-focused design. They deliver high-quality, innovative digital products that boost customer experience and client engagement.
Their team of over 100 skilled professionals includes engineers, project managers, and designers who work collaboratively to meet client needs and exceed expectations. This collaborative approach has helped Blink22 maintain a high level of customer satisfaction and secure repeat business from clients across the globe Additionally, their commitment to diversity, with a significant portion of leadership roles held by women, sets a strong example for creating an inclusive and supportive work environment.
DevriX
DevriX is a Bulgaria-based WordPress development agency specialising in enterprise-level web development, WordPress consulting, and digital strategy services. They work with businesses of all sizes, from startups to large enterprises, helping them build scalable and high-performance WordPress websites and web applications.
They have successfully implemented a large-scale content management system (CMS) for a multinational corporation, enabling efficient content creation, publishing and management across multiple websites and regions within a unified WordPress platform.
Tip:
- Search company databases to find more competing companies. These can be free, like company.info, or paid, via chambers of commerce (such as the Dutch Kamer van Koophandel) or commercial databases like Bold Data. Identify which databases match your search best and use them to create a list of potential customers to target.
Which products are you competing with?
In web design and web application development services, the product is the service. This means that the real question is: what makes one service provider different from another? The answer is: technical knowledge, available capacity, references, domain knowledge, flexibility, scalability, reliability, communication and language capabilities, quality management, security infrastructure, vertical and/or horizontal market focus and niche market orientation, among other things. The service provider’s location is also an important factor.
Tips:
- Invest in country branding (sometimes also called nation branding). You can do that by contacting relevant export promotion agencies from your country to connect with country branding efforts or campaigns. For more information, see our tips on doing business with European buyers.
- Find out how to get a competitive advantage, based on factors such as quality, cost, technology or product characteristics. For ideas, study the annual Developer Skills Report. This includes the most popular programming languages and frameworks and the kind of frameworks hiring managers want versus the frameworks developers know (so you can see where there is more demand than supply).
4. What are the prices of web design and web application development on the European market?
Because web design and web application development services are a commodity, the market is a bit more price sensitive than other IT outsourcing markets. It makes the market more difficult to enter as competition is very strong (both locally and internationally). The price pressure is high. In any case, the price must be right and competitive. The price is influenced by technological requirements, skill levels, project complexity, length of the contract and other requirements written in the Service Level Agreement (SLA).
First determine your costs. You have fixed costs (like software licenses, hardware and office space), variable costs (like hosting services, domain registrations and subcontractors). Your offer should include a breakdown of the costs, with your hourly rates and an honest estimation of the number of hours you expect to work on the project.
Then you must choose a price model for your product or service. There are 4popular working models: Fixed-Price, Time and Materials, Incentive Based and Shared Risk-Reward. The most common price model for these services is a fixed-price contract: an all-inclusive offer, where clients are billed based on pre-defined (in the SLA) milestones.
Keep in mind that if the project uses Agile, there is no pre-determined specification, which makes estimation a big challenge.
The average annual salary of a software developer in western Europe lies around €56,000. For web designers, the salaries lie around €60,000 per year, web application developers earn a bit more, hitting almost €70,000 per year. In offshore destinations, the salaries are usually significantly lower. This means that outsourcing to countries where wages are lower can lead to considerable cost savings.
If you focus on a niche or non-commodity market, European buyers are often less price sensitive.
Tips:
- Study average prices in reports such as those by Cleveroad, Qubit Labs, and IT Jobs Watch. You can also research the average salaries for various roles via platforms like Payscale or read documents like this one on web developer salaries in Latin America and Asia.
- Create the “ideal” client persona to help you tailor your offer. For example: “a software development company with fewer than 200 staff members, in the Munich area, specialised in ERP development/customisation using Microsoft Dynamics AX”.
- Choose a type of price model for your outsourcing contract. For more information, see this paper on pricing models in outsourcing. Go beyond setting the right price and work out your pricing strategy. This should include, for example, your and your clients’ preferred pricing model, payment terms and expectations, and how/when you offer discounts.
Globally Cool carried out this study in partnership with Laszlo Klucs on behalf of CBI.
Please review our market information disclaimer.
Search
Enter search terms to find market research