
Entering the European market for software development services
You must comply with mandatory requirements, such as copyright law and the General Data Protection Regulation. Buyers may have additional requirements regarding issues such as quality management and corporate social responsibility (CSR), as well as industry-specific standards. The most promising way to enter the market is by working with a strategic partner. As competition is strong, you should differentiate on quality and specialise to reduce competition.
Contents of this page
- Which requirements and certifications are necessary for software development services to be allowed on the European market?
- Channels can you use to get software development services onto the European market?
- What competition do you face on the European software development services market?
- What are the prices of software development services on the European market?
1. Which requirements and certifications are necessary for software development services to be allowed on the European market?
On the European market for software development services, requirements vary per industry, segment and even country. Listing all regulations would be impossible; there are a lot and new legislation is always in the making.For more information, see our study about which requirements outsourcing services need to comply with to enter the European market.
What are mandatory requirements?
Mandatory outsourcing requirements can be legal or non-legal. Legal requirements include legislation about copyright and data protection. Non-legal requirements mainly deal with security, but also ethics. Although you are not obliged to comply by law, all requirements mentioned here are considered minimum requirements to enter the European market.
Copyright: Computer Programs Directive
The European Union (EU) has established legislation to protect computer programs by means of copyright. This Computer Programs Directive says existing computer programs may not be copied by others. It was issued under the internal market provisions of the Treaty of Rome. The most recent version is Directive 2009/24/EC.
According to the Directive on the legal protection of computer programs, you have to make sure not to breach any copyright when placing your computer program (software) on the market.
Tips:
- Read more about the legal protection of computer programs on the European Commission’s website.
- Check the exact regulations in your target market. All EU member states have implemented the directive into national legislation. Although they are generally the same, there could be minor differences.
- Pay attention to copyright and infringement (the act of breaking or disobeying the contract) clauses in the contracts you sign with European buyers.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is designed to protect the privacy of individuals in Europe from data leaks. It is also incorporated into the European Economic Area (EEA) Agreement. This means the GDPR is also enforced in Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway. France has its own France Data Protection Act.
Under the GDPR, any company or individual that processes data is responsible for the protection of this data. While not all big data projects concern personal data, many of them do. Data includes the following: names, email addresses, bank details, social media content, photos, and IP addresses. As the personal data aspect in big data development is expected to grow, complying with the GDPR is very relevant for you.
It is expected that within the next few years, around 75% of the world’s population will be subject to regulations similar to the GDPR. This means that protecting data and privacy will not only be necessary in the EU but also in most countries worldwide.
Tip:
- Read more about this topic in the buyer requirements study.
ePrivacy Regulation
The ePrivacy Regulation is the replacement of the ePrivacy Directive, commonly known as the “cookie law”. It contains specific regulations for data protection in the electric communications sector. For example, it prohibits unsolicited commercial electronic messages (“spam”). It contains strict rules on cookies, and contact details may only be published with the subject’s consent.
Tip:
- Keep track of the latest legal requirements drawn up by the European Commission. You can also search their website to find all their policies on the market for software development.
Security
Data security is one of the main challenges for software development service providers. This includes both data protection and recovery systems. Many European buyers expect you to implement an information security and management system, especially in industries in which security is essential, such as finance and banking, or healthcare. Although there is no specific legislation on this, the ISO 27000 family contains common standards and guidelines for information security.
ISO 27001 is an internationally recognised standard that provides requirements for an information security management system. Companies can become ISO 27001 certified if they comply with the standard. ISO 27002 is a supporting document to ISO 27001 that gives guidance and advice on the implementation of information security controls. Other supporting guideline documents are ISO 27003 and ISO 27004.
ISO 27701 is set to be the go-to standard for compliance with GDPR regulations, in the same way that ISO 27001 is considered to be the 'golden standard' for information security management.
Tips:
- Make sure you have effective security processes and systems in place, from business continuity and disaster recovery to virus protection.
- Ask your buyer to what extent they require you to implement a security management system like the ISO 27001 standard.
- Consider obtaining the ISO 27701 certification. To do so, you must either have an existing ISO 27001 certification, or implement ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 together as a single implementation audit.
Ethical use of data
Software development is also based on data. Data does not equal facts. Data can be biased. This can lead to ethical dilemmas that need to be addressed.
Imagine a software development company creating an algorithm to assist with hiring decisions for a tech company. The company trains its algorithm using historical hiring data, which unfortunately contains biases against certain demographics, such as gender or race. Due to these biases, the algorithm learns to favour candidates from specific demographics over others, despite their qualifications.
When this software is used in their client's hiring process, it unknowingly rejects qualified candidates from underrepresented demographics, that will result in inequality in their workforce. This can lead to various negative consequences, including lawsuits, damage to the company's reputation, and a less diverse and innovative workforce.
Software developers should proactively address biases in their data and algorithms, strive for diversity and inclusivity, and continuously evaluate and lower potential ethical risks throughout the development process.
Data privacy is one of the main ethical issues with software that is based on big data. To prevent big data from being used for the wrong purposes, we need to implement ethics into the code.
The different applications and uses of big data evolve so fast that you must keep up with its developments. European buyers expect you to stay on top of the developments so you can deliver ethical services to them.
Tips:
- Read more about big data in software development to see where big data can benefit your product and services, but also to find out how to deal with ethics surrounding the use of big data.
- If you are working with big data for software development: stay up to date on the topic of Ethics in AI. The Council of Europe is a good source to start. Or the Ethical Guidelines for trustworthy AI by the European Commission. And do not forget the Artificial Intelligence Act, on which the European Commission is currently working.
- Prioritise ethical considerations when you work with big data. This way you can build trust with your buyers. You can prioritise data privacy, strive for objectivity, be transparent and accountable and continuously assess and improve your ethical practices.
Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive and Forced Labour Regulation
Important upcoming Green Deal legislation includes the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) and the Forced Labour Regulation. In February 2022, the European Commission adopted a proposal for a CSDDD. This means larger companies have to identify and – where necessary – prevent, end or reduce any negative impacts of their activities on human rights and the environment. Both in the company’s own operations and in its value chains. This means that the new rules may apply to you indirectly via your buyers.
In September 2022, the European Commission proposed a new Forced Labour Regulation. Complementing the CSDDD, this regulation bans products made with forced labour from the EU market.
As these proposed laws have yet to be finalised and approved, their exact implications are not yet clear. Before they can enter into force, they must be formally approved by the European Council. Nevertheless, you should familiarise yourself with the proposals and be prepared for their rollout.
Tips:
- Read more about the CSDDD.
- For details on the Forced Labour Regulation, check out the questions and answers and factsheet.
- Stay up to date on the proposed rollout of the new CSDDD and the Forced Labour Regulation.
What additional requirements do buyers often have?
Most European buyers of software development services have additional requirements regarding technical knowledge and experience, project management, quality, and corporate social responsibility (CSR).
Technical knowledge and experience
As a software development service provider, you must stay on top of the developments in the market. You need to stay informed on the latest technologies, platforms, frameworks and innovations, and keep your skills up to date.
Tips:
- Stay up to date on the latest software technologies and trends, like quantum computing.
- Provide references, testimonials and examples of recent work, preferably on your website, as European companies often require proof of your technical skills.
Soft skills
Buyers of software development services look for developers who not only know their technical stuff but also have good people skills (also known as soft skills). This is because clear communication and teamwork help developers understand what clients need and work well together. Being able to talk to clients nicely also builds trust and keeps them coming back.
Soft skills like problem-solving and flexibility help developers tackle tricky issues and adapt to changes in projects. Understanding what users want and making software easy to use is also important. Good leadership and teamwork skills keep everyone on track and motivated, so make projects run smoothly.
Agile project management
European buyers may expect you to work according to the Agile concept. This is based on the Agile Manifesto, which represents the ability to respond to change. It focuses on how people work together, letting solutions evolve through collaboration between self-organising and cross-functional teams.
Agile software development advocates adaptive planning, visualisation, evolutionary development, early delivery and continual improvement. Scrum is the most widely used Agile framework.
Quality management systems
Some European buyers only do business with companies that have a quality management system. Examples of systems that are relevant for software development services are ISO/IEC 25000 (SQuaRE), IEEE 730, IEEE 1061, ISO 9001:2015 and the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI).
Tip:
- Read more about these quality management systems in our buyer requirements document.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Most European buyers of software development services will appreciate certification related to Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). Some even require it. Here you can read what it is, why it is important and how you can get it: Tips on how to go green in the outsourcing sector and Tips on how to become a socially-responsible exporter in the outsourcing sector.
What are the requirements for niche markets?
European buyers often require you to comply with a sector- and/or industry-specific standard or code of practice. There are also many technologies, technical standards, protocols and frameworks related to software development. They are developed and maintained by various organisations, and they can differ significantly.
Read more about the requirements for niche markets in the buyer requirements study.
2. Channels can you use to get software development services onto the European market?
The European market for software development services can be divided into horizontal and vertical market segments. You can enter these segments through several different market channels. The most realistic market entry channel for you is working with a strategic partner.
How is the end market segmented?
The market for software development services can be segmented by horizontal market (type of service) and by vertical market (type of industry).
Figure 1: Horizontal and vertical market segments with opportunities for service providers
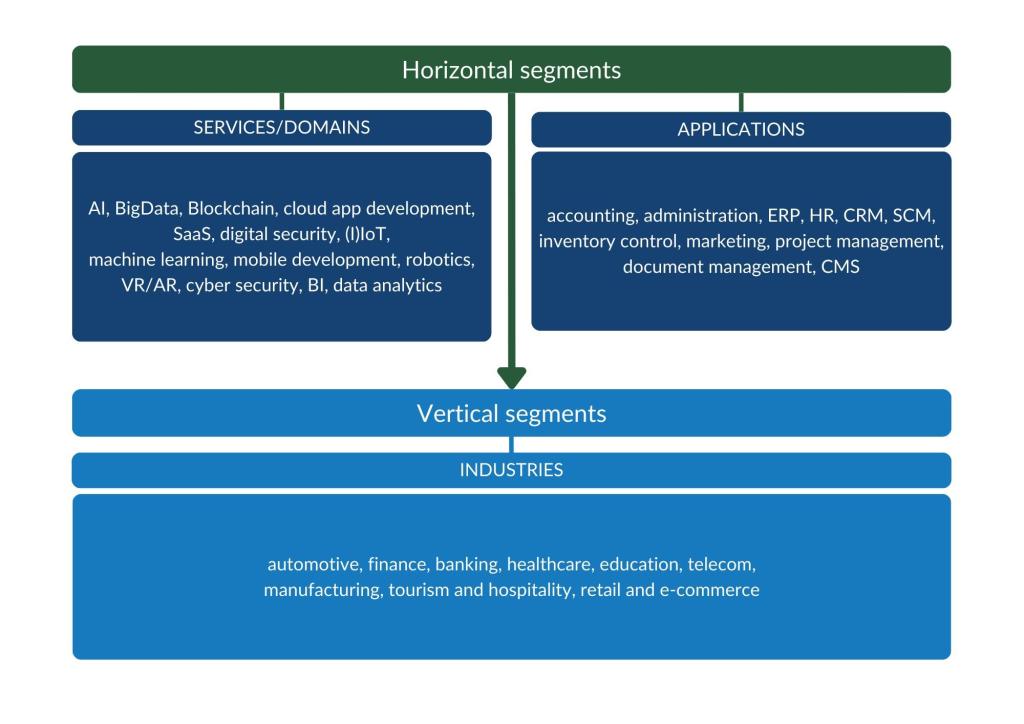
Source: Globally Cool
The most promising horizontal markets are AI, big data, blockchain, cloud, digital transformation, (I)IoT, machine learning, mobile development, robotics and VR/AR. It is difficult to say which offers you the best opportunities. Software as a Service (SaaS) / cloud development is interesting because demand is high. However, the European market has a lot of SaaS/cloud service providers, so competition is strong. The same applies to mobile development, as these are basically commodity services.
On the service provider side, there are generalists and specialists. Specialists focus on (and have extensive experience in) a specific vertical or horizontal market. Generalists, on the other hand, do not specialise in any particular segment but focus on various (high in demand) technology.
Opportunities to sell your own human resources (HR), enterprise resource planning (ERP), accounting or administration software are limited. However, positioning your company as a specialist in these fields strengthens your offer as a provider of software development services.
Tips:
- Monitor relevant developments in the European software development market via Google searches that combine your service/product with a particular niche market.
- Research the end-market segment you want to focus on, so you can effectively market your company. Subscribe to the mailing lists of organisations that combine that end-user industry with technological solutions, such as the British Health Tech Association.
- If your service is a relative commodity, you should focus on a niche market. Especially if you can find a niche market that is underserved with software or has the room/need for digital transformation.
Through which channels do software development services end up on the end market?
There are various channels through which software development services end up on the end market, see figure 2. This trade structure is very similar in every European country. Working with a strategic partner is your most realistic market entry channel.
Figure 2: Trade structure for outsourcing software development services in the European market
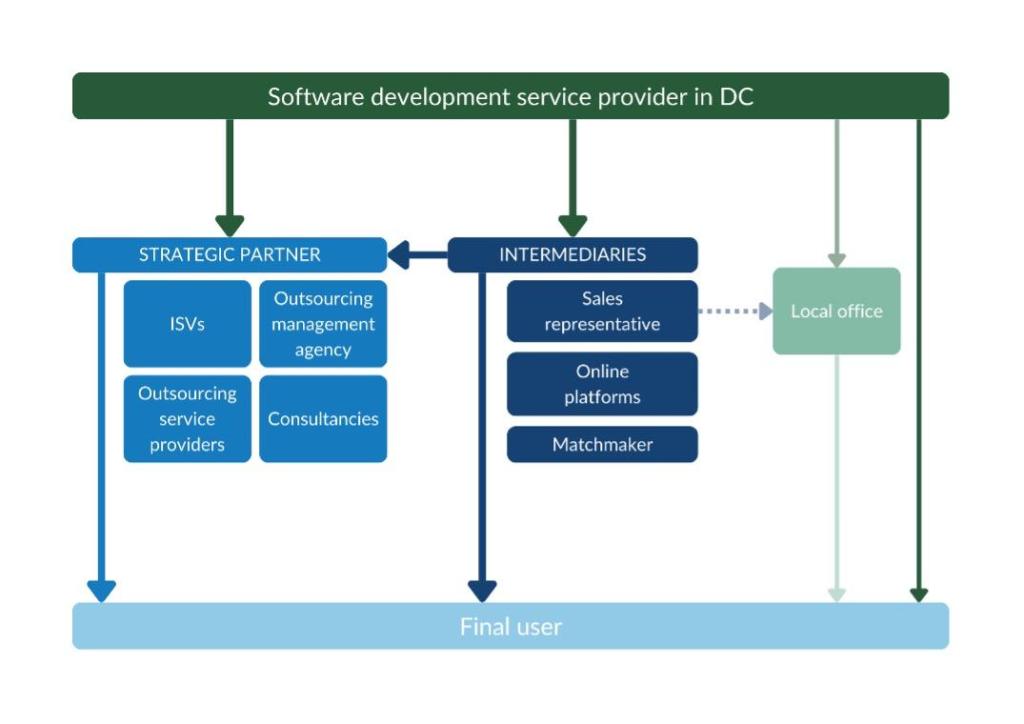
Strategic partner
Working with a strategic partner is your most realistic market entry channel. They could be Independent Software Vendors (ISVs), outsourcing management agencies, outsourcing service providers or consultancies.
A provider that is similar to your company would be most suitable. Ideally, this company should design, develop, market, sell and maintain its own software products and offer IT services that are similar to yours.
The relationship between a strategic partner and a subcontracted supplier (you) is generally characterised by:
- Trust;
- Interdependence;
- A structured relationship (functions, tasks, communication and procedures);
- Potentially limited marketing visibility and market access opportunities for the subcontracted supplier;
- No intellectual property (IP) rights, or a loss of IP rights for the subcontracted supplier;
- When there is no guaranteed amount of work, work orders are on an if/when-needed basis.
Please note that when you work with a strategic partner, they communicate with the final user of the software you are developing. You are merely a subcontractor. The ITO service provider (you) will not appear in marketing communications of the strategic partner. You will be referred to as ‘delivery centre’.
You can find a strategic partner either directly or by working with an intermediary. Because many European companies prefer to deal with a local contact person, an intermediary is a good option.
Tips:
- Attend leading (online) European trade fairs, such as Qton London, JAX London and JS World Conference in Amsterdam to meet competitors and potential customers. Do your homework and select events that fit your profile. Make a list of relevant events using trade event directories, such as 10Times and UK Exhibitions, and update it regularly.
- Use IT industry associations to find potential customers, such as Bitkom in Germany, NLdigital in the Netherlands, and techUK and BIMA in the United Kingdom (UK). If you specialise in a particular industry, you can also use associations for that niche, such as the Association of British HealthTech Industries.
- Use outsourcing associations to find potential customers, such as the Global Sourcing Association, the German Outsourcing Association and Sourcing Nederland.
Intermediary
You can work with an intermediary to find a buyer. This is different from working with a strategic partner as the final user of your software will most likely not know your name, because you are ‘just’ the subcontractor. However, you can use an intermediary to find a strategic partner. Examples of intermediaries are sales representatives, online platforms and matchmakers.
Sales representatives
They are more involved in the sales process than matchmakers. When working with a sales representative:
- The sales representative contacts prospects for you;
- The sales representative also makes the sales and sometimes manages projects to a certain degree;
- You pay a retainer and a success fee (which can be expensive), or a fixed monthly fee;
- The sales representative can have multiple clients or work exclusively for you.
A good sales representative has a large, relevant network, so they do not make cold calls. Their success fee is often a percentage of the projects they bring in. Hiring a sales representative will increase your expenses, but you will be free to focus on your core business and search for other markets yourself.
Online platform
Electronic marketplaces are a cheap marketing tool that may make direct sales easier. They can also help you find companies to work for. Possibly as an independent consultant (someone from your team), or as a subcontracting team. These platforms used to focus on freelancers but are increasingly suitable for SMEs.
Matchmaker
A matchmaker is a person or company with many relevant contacts in a specific market segment or industry. As an intermediary, they are a “door opener” and not an agent to make cold calls or send cold emails. You have to properly inform your matchmaker about your company. They speak with many potential customers and often create long lists of potential outsourcing providers. The more information they have on your company and the better they understand your capabilities, the more they can spread the word about you.
If you work with a matchmaker:
- The matchmaker makes appointments with prospects for you;
- The presentation and sales process remains in your own hands;
- You pay a retainer and a success fee (which can be expensive);
- The matchmaker usually has multiple clients;
- You need to set clear expectations and goals (and exit criteria) to measure their performance.
A retainer + success fee can be expensive. While the success fee depends on what the intermediary has delivered, you must pay the retainer (usually a fixed monthly payment) regardless of their performance. Together, they should provide a strong motivation for the intermediary to deliver: the retainer should be high enough to cover some of the costs, but low enough to encourage delivery. A properly drafted contract, by a lawyer, is a must!
You also need to determine an exit strategy in the contract, with a clearly defined period after which the contract can be terminated without any further consequences. This period is usually not longer than 3 or 4 months, after which the contract will be evaluated and can be terminated or prolonged. For this period, there should be clearly defined delivery expectations and targets for the consultant/matchmaker (such as the number of relevant contacts, meetings and leads). You could also negotiate a trial period.
Tips:
- Be cautious if intermediaries only ask a success fee for their work, because either they are excellent at their job, or they are desperate and may not (be able to) deliver. You should also be cautious if intermediaries want to work for you part-time besides their regular job, because they are often so busy that they do not deliver.
- When contracting an intermediary, involve a good lawyer who knows the applicable law of the country where the intermediary resides and has experience with this type of contracting. Pay special attention to exit clauses, success criteria, deliverables and payments.
- Try to avoid limitations to your marketing coverage and activities in your contracts.
- Some food for thought: although convenient, your uncle who lives in Germany might not be the best intermediary for your company.
Local office
Ideally, you should establish a local office in your European target market. You can also choose to open an office in one of Europe’s nearshoring destinations as this is generally cheaper.
A local presence makes it easier to build long-term relationships with customers through personal contact. It also increases your credibility, builds trust and allows you to retain complete control over your marketing and sales activities. However, this is very difficult in practice, as it requires a lot of experience and large investments. Most companies in developing countries are simply too small and do not have the financial strength or enough verified market opportunities for this.
Tips:
- Be aware that establishing a local sales office is very costly and you need a strong financial position.
- Consider establishing your own office if you have already established a client base in the target market, or if you have a well-founded indication of the demand for your services/products. If you decide to establish an office, involve your sales/marketing representative.
- Look for alternatives to lower your costs, such as business incubators or government incentives to bring your business to a particular country/region.
Direct sales
You can also try to sell your software development services directly to European end users. Many European companies are looking for cost reduction and delivery capacity, which developing countries can often provide. This is one of your unique selling points (or at least a competitive selling point). However, you should be aware that these end users might not have qualified IT staff to work with.
Direct sales require experience in the European market and are most suitable for relatively large providers that want to target large European end users. Your best bet is to focus on a small, underserved niche market. For most suppliers from developing countries, however, it is very challenging to sell software development services directly. Sometimes, they work together to make a direct sales offer. Having one or more existing customers in Europe will help, as references are a must for direct sales.
Tips:
- Combine offline and online promotion channels to develop as many contacts as possible. This maximises your chances of finding suitable partners/customers. Use social media platforms as a marketing tool. LinkedIn can be particularly useful for making initial contacts and conducting market research.
- Have a professional, high-quality company website, where you can present full, accurate and up-to-date details of your offering at low cost. Make it compatible with mobile devices and invest in Search Engine Marketing and Optimisation (SEM/SEO), so potential customers can easily find you online.
- Look for potential leads on online platforms like Appfutura and Talent Alpha (specialised in SMEs), or UpWork, Freelancer, Fiverr, ITeXchange, Clutch, and pliXos.
What is the most interesting channel for you?
Selecting a channel depends on your type of company, the nature of your product or service, your target market, and your available resources for market entry. Regardless of the channel you choose, your own marketing and promotion is a vital part of your market entry strategy, for which you are responsible.
3. What competition do you face on the European software development services market?
Competition in the software development services market is strong. Besides competition on price and quality, there is also competition based on location.
European companies generally prefer outsourcing to providers within their country. When they do outsource to companies abroad, they usually prefer nearshore locations, because of proximity, language, cultural similarities and the minimal time difference.
Which countries are you competing with?
Your strongest competing countries are India, China, Philippines, Poland, Egypt and Bulgaria.
The Global Services Location Index (GSLI) ranks the competitiveness of ITO/BPO destinations based on 4 categories: financial attractiveness, people skills and availability, business environment and digital resonance.
Table 1: Global Services Location Index
| Financial attractiveness (35%) | People skills and availability (25%) | Business environment (25%) | Digital resonance (15%) |
| Compensation costs | ITO/BPO experience and skills | Country environment | Digital skills |
| Infrastructure costs | Labour force availability | Country infrastructure | Legal and cybersecurity |
| Tax and regulatory costs | Educational skills | Cultural adaptability | Corporate activity |
| Language skills | Security of IP | Outputs |
India
India was expected to have the largest software developer population in the world by 2024, but is surpassed by China. India continues to lead the GSLI, mainly due to the combination of excellent English language skills and low-cost services. However, China is already scoring better in all other categories.
Software developer rates in India are among the lowest in the world at €10 (for junior developers) to €35 per hour. European buyers often associate these extremely low rates with poorer project quality. They think that cheap service providers must compromise on the skills and experience of the developers, or on their working circumstances. This is reflected in the fact that Indian professionals rank 31st in the best developers in the world.
This illustrates that, although offering competitive rates is important, you should not compete only on price. India has consistently provided low-skilled staff for traditional tasks, but the current digital transformation requires highly skilled professionals. As relatively simple tasks can be automated, you should focus on excellent skills, knowledge and creativity, which have a higher value. Demonstrating your commitment to quality through references and quality management systems is key to building trust among potential European clients.
India is working hard on its talent pool. The government has introduced initiatives like PM Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 to train 4.7 million individuals in advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), 3D printing, drones, and the Internet of Things (IoT) as part of the fourth industrial revolution (i4.0).
India is using its strong foundation in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education to further educate young students on advanced technologies like cryptocurrency and AI, aligning with the objectives stated in the National Education Policy for 2020. Additionally, the implementation of the new National Data Governance Policy aims to position India as a competitive market with a high-skilled workforce at relatively lower to mid-level costs. This helps to advance the country's ambition to become a leader in AI innovation through initiatives like "Make AI in India."
China
China is home to the largest, fastest-growing software developer population in the world. The runner-up in the GSLI is catching up with India, performing well in all areas. With a score of 100%, Chinese software developers rank first on the HackerRank's best developer list.
However, if the trade conflict between the United States (US) and China and its technology companies continues, this may deter global investors. The size of their future workforce is also concerning, because due to China’s one-child policy population growth is slowing down. This combined with the relatively average English proficiency in China, and you still have good opportunities to compete.
Philippines
The Philippines rank 12th in the 2023 GSLI. They have been performing strong for a few years in a row. The Philippines are originally more of a BPO destination, but their IT sector is developing strongly as well. They are culturally relatively close to the United States of America and Western Europe, which makes collaboration relatively easy.
They are still very cost-competitive and have a strong supply of software developers. With a score of almost 64%, the quality of software developers from the Philippines is ranked 46th, between Colombia and Malaysia. They have excellent English language skills.
Egypt
Egypt is a strongly emerging African destination for software development offshoring. Its time zone (GMT+2) partly overlaps with western and northern Europe, eliminating the time differences generally associated with offshoring. The country ranks 23rd in the GSLI; this is 8 places lower than in 2021. This is mainly due to a lack of digital focus. The country aimed to invest heavily in IT, but so far it has not led to good results.
The labour costs are rising, the Egyptian currency is not doing very well and public debt has grown significantly in the past few years. But the country is home to a large technically-educated workforce that is skilled in English, Arabic, French, German and other European languages. With a score of more than 69%, the quality of Egyptian software developers is ranked 42nd, between New Zealand and South Africa. The hourly software development rates in Egypt are relatively low; comparable to Asia.
Tips:
- Compete on the quality of your services, rather than just on costs.
- Specialise in specific horizontal/vertical markets, emerging technologies and/or niche market segments to avoid competition.
- Visit the websites of IT outsourcing associations and software development associations to get a better understanding of competing countries. Examples are the Central and Eastern European Outsourcing Association (CEEOA) and the outsourcing destinations page of the German Outsourcing Verband.
Which companies are you competing with?
Examples are:
- Exist;
- Mindbowser; and
- Orchtech.
Exist
Exist is a leading technology innovation and software development company headquartered in Manila. They specialise in providing custom software solutions, product development, and IT consulting services to clients worldwide. Exist has expertise in various industries including healthcare, fintech, logistics, and e-commerce. They are known for their commitment to quality and innovation, using technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and blockchain to deliver advanced solutions to their clients.
Mindbowser
India-based Mindbowser is a good example of an initially small company that has managed to successfully enter the European market. Mindbowser provides a range of software development services, including mobile app development, web development, AI solutions, and IoT applications.
Mindbowser has been focusing on delivering high-quality, tailor-made solutions for both start-ups and established businesses. The company works with agile development processes and a customer-centric approach.
Orchtech
Egypt-based Orchtech is an Agile software development company with clients across Europe. They offer English- and French-speaking developers, who are university graduates in software engineering or computer science. Orchtech provides software outsourcing services via staff augmentation and project-based models. Their homepage highlights some of the company’s international clients, and Orchtech’s commitment to CSR and innovation.
Tip:
- Search company databases to find more competing companies. These can be free, like company.info, or paid, via chambers of commerce (such as the Dutch Kamer van Koophandel) or commercial databases like Bold Data. Identify which databases match your search best and use them to create a list of potential customers to target.
Which products are you competing with?
In software development, the product is the service. This means that the real question is: what makes one service provider different from another? The answer is: technical knowledge, available capacity, references, domain knowledge, flexibility, scalability, reliability, communication and language capabilities, quality management, security infrastructure, vertical and/or horizontal market focus and niche market orientation, among other things. The service provider’s location is also an important factor.
Tips:
- Invest in country branding (sometimes also called nation branding). For more information, see our tips on doing business with European buyers.
- Find out how to get a competitive advantage, based on factors such as quality, cost, technology or product characteristics. For ideas, study the annual Developer Skills Report. It includes the most popular programming languages and frameworks, and the kind of frameworks hiring managers want versus the frameworks developers know (so you can see where there is more demand than supply).
4. What are the prices of software development services on the European market?
Multiple buyers of software development services in Europe have shared that price is not the most important criterion. If they choose an outsourcing provider from a developing country however, they are happy the price is lower, but they still find communication and skills much more important.
So, although price is often not the most important selection criterion, it must be right and competitive. The biggest price component in any software development outsourcing project will be person-hours. That is the number of specialists and the effort they need to complete each task.
The price is influenced by technological requirements, skill levels, project complexity, length of the contract and other requirements written in the Service Level Agreement (SLA). Your offer should include the price, with your hourly rates and an honest estimation of the number of hours you expect to work on the project.
You must also choose a price model for your product or service. There are 4 popular working models: Fixed-Price, Time and Materials, Incentive Based and Shared Risk-Reward. The most common price model for software development is a fixed-price contract: an all-inclusive offer, where clients are billed based on pre-defined (in the SLA) milestones.
There are various reasons to choose one price model over the other. It all depends on your personal situation. There are some sources to help you choose the best price model for you.
The average annual salary of a software developer in western Europe lies around €56,000. In offshore destinations, the salaries are usually significantly lower. This means that outsourcing to countries where wages are lower can lead to considerable cost savings.
If you focus on a niche or non-commodity market, European buyers are often even less price sensitive.
Tips:
- Study average prices in reports such as those by Cleveroad, Qubit Labs, and IT Jobs Watch. You can also research the average salaries for various roles via platforms like Payscale.
- Create the “ideal” client persona to help you tailor your offer. For example: “a software development company with fewer than 200 staff members, in the Munich area, specialised in ERP development/customisation using Microsoft Dynamics AX”.
- Choose a type of price model for your outsourcing contract. For more information, see this paper on pricing models in outsourcing. Go beyond setting the right price and work out your pricing strategy. This should include, for example, your and your clients’ preferred pricing model, payment terms and expectations, and how/when you offer discounts.
Globally Cool carried out this study in partnership with Laszlo Klucs on behalf of CBI.
Please review our market information disclaimer.
Search
Enter search terms to find market research