
Entering the Dutch coffee market
Only 36% of coffee imports entering the Netherlands is sourced directly from producing countries. These imports come mainly from the world’s largest coffee producers: Brazil, Vietnam and Colombia. Sustainability is very important on the Dutch market, making the Netherlands an important market for certified coffees. At the same time, the demand for high-quality coffees is increasing. Therefore, higher-quality coffees and sustainable coffee may find interesting market opportunities in the Netherlands.
Contents of this page
1. What are the requirements for coffee to enter the Dutch market?
You can only export coffee to the Netherlands if you comply with strict European Union requirements. Buyer requirements can be divided into:
- Musts: legal and non-legal requirements you must meet to enter the market;
- Additional requirements: those you need to comply with to stay relevant in the market;
- Niche requirements: applying to specific niche markets.
The highlights for these requirements are given below, specified for the Dutch market where relevant.
1. Legal and non-legal requirements you must comply with
Legal requirements
You must follow the European Union legal requirements applicable to coffee. These rules mainly deal with food safety, where traceability and hygiene are the most important themes. Special attention should be given to specific sources of contamination, namely:
- Pesticides — consult the EU pesticide database for an overview of the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for each pesticide;
- Mycotoxins/mould, particularly Ochratoxin-A (OTA);
- Salmonella (although coffee is considered low-risk).
Quality requirements
Green coffee is graded and classified for quality before export. There is no universal grading and classification system for coffee. The Specialty Coffee Association’s standards for green coffee grading are often used as a point of reference. However, most producing countries have and use their own grading systems.
According to the International Trade Centre (ITC), grading is usually based on the following criteria:
- Altitude and region;
- Botanical variety;
- Preparation — wet processed (washed), dry processed (natural), semi-washed (wet-hulled), pulped natural or honey processed;
- Bean size or screen size, sometimes also bean shape and colour (note: screen size is important to ensure that coffee batches are uniform in size, which allows for uniform roasting which improves the quality of the final product);
- Number of defects or imperfections;
- Roast appearance and cup quality in relation to flavour, characteristics and cleanliness;
- Bean density.
Specialty coffee is also graded according to its cupping profile. Fragrance, flavour, aftertaste, balance, acidity, sweetness, uniformity and cleanliness are important factors in the grading process. If you sell specialty coffee, it is important for buyers to know the cupping score of your coffee. Although not mandatory, adding this information to the documentation of the coffee you are exporting might add value. It is very important to be aware of the quality of your coffees, either through local cupping experts or by becoming a cupping expert yourself.
Note that there is no exact definition of specialty coffee within the coffee industry. The Coffee Quality Institute and the cupping protocols of the Specialty Coffee Association consider that coffees graded and cupped with scores below 80 are considered standard quality and not specialty. Nevertheless, the exact minimum scores defining specialty coffee differ per country and per buyer. Some buyers consider 80 too low and demand a cupping score of 85 or higher.
Labelling requirements
Labels of green coffee exported to the Netherlands should be written in English and should include the following information to ensure traceability of individual batches:
- Product name
- International Coffee Organisation (ICO) identification code
- Country of origin
- Grade
- Net weight in kilograms
- For certified coffee: name and code of the inspection body and certification number
Figure 1: Examples of green coffee labelling

Source: commodity.com
Packaging requirements
Green coffee beans are traditionally shipped in woven bags made from jute or hessian natural fibre. Jute bags are strong and robust. Other materials, such as Grainpro or other innovative material like Videplast liners, are often used to pack specialty coffees inside jute bags.
Most green coffee beans of standard quality imported into the Netherlands are packed in container-sized bulk flexi-bags that hold roughly 20 tonnes of green coffee beans each. The rest of the green coffee is transported in traditional 60 or 70 kg jute sacks, held in containers of 17 or 19 tonnes, respectively.
Other packaging used in transporting coffee includes polypropylene super sacks for 1 tonne of coffee, polyethylene liners for 21.6 tonnes and vacuum-packed coffee. These techniques provide two advantages in the coffee trade, namely increasing efficiency and maintaining or preserving quality.
Figure 2: Examples of coffee packing: jute bag, container-sized flexi bag, GrainPro and Videplast liner

Sources: raadtradingco.com, bls-bulk.com and GrainPro
Tips:
- For the full buyer requirements, read the CBI study on buyer requirements for coffee in Europe or consult the specific requirements for coffee on the European Commission website of Access2Markets.
- Check EUR-Lex for more information on limits for different contaminants. For specific information on the prevention and reduction of Ochratoxin A contamination, refer to the Codex Alimentarius CXC 69-2009.
- For information on safe storage and transport of coffee, refer to the website of the Transport Information Service.
- Read more about quality requirements for coffee on the website of the Coffee Quality Institute.
2. Additional requirements
Additional food safety requirements
Expect buyers in the Netherlands to request extra food safety guarantees from you. Regarding production and handling processes, you should think of:
- Implementation of good agricultural practices (GAP): The main standard for good agricultural practices is GLOBALG.A.P., a voluntary standard for certification of agricultural production processes that provide safe and traceable products. Certification organisations, such as Rainforest Alliance, often incorporate GAP in their standards.
- Implementation of a quality management system (QMS): A system based on Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is increasingly required by buyers as a minimum standard for green coffee production, storage and handling. The implementation of regular checking of residue levels in your green (and roasted) coffee is an example of what could be part of this system. Especially monitor (and aim to prevent) Ochratoxin-A (OTA), polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and glyphosate contamination. It is recommended to proactively obtain certificates of analysis periodically for the coffee you produce and export, preferably from an EU-accredited laboratory such as Eurofins or Tüv.
- For roasted coffee, HACCP might be required, and sometimes complemented by a certification of the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) such as: BRC Global Standard Food Safety, FSSC 22000, IFS Food or SQF.
It is good to keep in mind that your Dutch importer might re-export large quantities of green coffee to other destinations in Europe. Those other buyers push their requirements forward to other players in the supply chain, which might increase the need for you to adopt other specific certifications or standards. This will depend on the final market and market channel used
Additional sustainability requirements
Corporate responsibility and sustainability are very important in the entire European coffee sector. In the Netherlands, coffee industry players will have sustainability policies highlighting their relationship with farmers, transparency in their operations, as well their social and environmental impact at origin. Examples of these company policies or codes of conduct are those of Pelican Rouge Coffee Roasters, UCC Coffee Benelux and Jacobs Douwe Egberts.
As an exporter, adopting codes of conduct or sustainability policies related to your company’s environmental and social impact may give you a competitive advantage. In general, it is likely that buyers require you to comply with their code of conduct, and/or fill out supplier questionnaires regarding your sustainability practices.
Certification standards are very often part of the sustainability strategy of traders, coffee roasters and retailers. As such, a standard like Rainforest Alliance/UTZ has become increasingly important in the mainstream coffee market. About 65 coffee supply chain actors operating in the Netherlands are Rainforest Alliance/UTZ-certified, among them traders like Greencof and Trabocca, and roasters such as Neuteboom Coffeeroasters and UCC Coffee Benelux.
Tips:
- Refer to the International Trade Centre Standards Map or the Global Food Safety Initiative website to learn about the different food safety management systems, hygiene standards and certification schemes.
- Find out which standards or certifications are preferred by potential buyers in your target segment. Buyers may have preferences for a certain food safety management system or sustainability label, depending on their end clients and/or distribution channels.
- Carry out a self-assessment to measure how sustainable your production practices are. You can fill out this online self-assessment form by Amfori BSCI to assess your social performance. This Excel form by the Sustainable Agriculture Initiative (SAI) Platform can be used to assess the sustainability performance of your farm.
- See our study on certified coffee for more information about the demand on the European market, trends and specific trade channels.
3. Niche requirements
Organic
In order to market your coffee as organic on the European market, it must comply with the regulations of the European Union for organic production and labelling. Obtaining the EU organic label is the minimum legislative requirement for marketing organic coffee in the European Union.
Note that the new EU organic regulation came into force on 1 January 2021. This means that producers in third countries will have to comply with the same set of rules as those producing in the EU. Also, inspections of organic production and organic products have become stricter to prevent fraud.
Before you can market your green coffee as organic, an accredited certifier must audit your growing and/or processing facilities. Refer to this list of recognised control bodies and control authorities issued by the EU to ensure that you always work with an accredited certifier. To become organic certified, you can expect a yearly inspection and audit, which aims to ensure that you comply with the rules on organic production.
Note that all organic products imported into the EU must have the appropriate electronic Certificate of Inspection (COI). These COIs must be issued by control authorities prior to the departure of a shipment. This requires you to get the necessary information, such as importer address and TRACES number, first consignee, and seal and vessel number of your container. If this is not done, your product cannot be sold as organic in the European Union and will be sold as a conventional product. COIs can be completed by using the European Commission’s electronic Trade Control and Expert System (TRACES), where you will also have to register as an organic exporter.
Fair trade
Before you can market your coffee as fair trade, an accredited certifier must audit your growing and processing facilities. The most common fair trade standard in the Dutch market is Fairtrade, for which the accredited certifier is FLOCERT. Fair for Life (by IMO/Ecocert) and Fair Choice (by Control Union) are other fair trade certifications that producers may choose. Although less recognised in the Dutch market, Fair for Life and Fair Choice have the advantage of lower costs, as the control bodies may combine the fair trade audit with the organic or Rainforest Alliance audit. However, always check demand and interest for a specific certification with your (potential) buyer. Also, in the case of Fair Choice and Fair for Life, check if and what kind of premium would be involved, as this is not regulated like in the case of Fairtrade’s minimum price.
Direct trade
The high-end specialty coffee segment is characterised by direct trade relations as well as high transparency and traceability from source to consumer. This means that buyers of these types of coffees ask for requirements that go beyond certification. Besides high quality, these buyers are interested in your stories about the origin of your coffee. This implies that you should know the specifics of your coffee and be willing to honestly share this information. Other than that, direct trade may result in more frequent coffee farm visits and product assessments by your buyers, as well as long-term business relations.
Tips:
- Learn more about organic farming and European organic guidelines on the European Commission website and the Organic Export Info website.
- Familiarise yourself with the range of organisations and initiatives that offer technical support to help you convert to organic farming. Start your search at the organic movement in your own country and ask if they have their own support programs or know about existing initiatives. Refer to the database of affiliates of IFOAM Organics to search for organic organisations in your country.
- Find importers that specialise in organic products on the website Organic-bio.
- Try to visit trade fairs for organic products, like Biofach in Germany. Check out their website for a list of exhibitors, seminars and other events at this trade fair. Here you will also find booths of the organic certification bodies.
- If you produce coffee according to a fair trade scheme, find a specialised Dutch buyer that is familiar with sustainable or fair trade products, for instance via the FLOCERT customer database.
- Try to combine audits in case you have more than one certification, to save time and money. Also investigate the possibilities for group certification with other producers and exporters in your region.
- Use this cost calculator to estimate what costs will be involved for your organisation to get Fairtrade-certified.
2. Through what channels can you get coffee onto the Dutch market?
The Dutch end market for coffee can be segmented by quality and by type of consumption: in-home and out-of-home consumption. The high-end segment represents a growing niche market in both the in-home and out-of-home segments, as consumers increasingly demand specialty coffees. Suppliers in producing countries mainly enter the Dutch market through importers or medium-sized and large roasters.
How is the end market segmented?
The Dutch end market for coffee can be segmented by quality, as shown in the figure below:
Figure 3: Coffee end market segmentation by quality
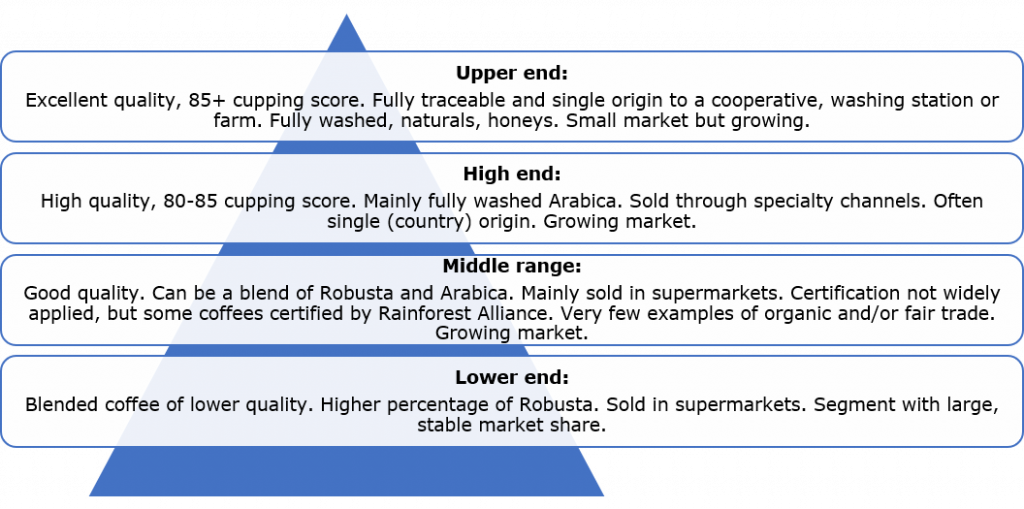
Source: ProFound
In the Netherlands, supermarkets are the main sales channel for coffee. In 2020, about 90% of coffee consumers in the Netherlands said they buy (some of their) coffee in supermarkets. Supermarkets have a wide variety of coffee products, ranging from low-end to high-end products. The largest supermarkets in the Netherlands are:
- Albert Heijn (parent: Ahold Delhaize, Netherlands/Belgium)
- Jumbo (owned by Van Eerd Group, Netherlands)
- Plus (part of Sperwer Group, Netherlands)
- Lidl (part of Schwarz Group, Germany)
- Aldi (part of Aldi Nord, Germany)
Low end: Coffees in the low-end segment are mainstream, low-quality and mainly blended coffees. These blends are characterised by high shares of Robusta beans. Besides some mainstream brands, also the lower-quality private label products from supermarkets belong to the low-end segment. In addition, most coffee pads and instant coffee belong to this low-end segment. Coffees in the low end of the market are mainly sold in supermarkets and through service channels, such as offices and universities.
Product and price examples in the low-end segment, based on Albert Heijn’s retail prices in 2021, include:
| Product | Retail price (€/kg) | ||
| Low end | Caféclub Naturmild (Ground coffee, UTZ-certified, 500-gram package) | 
| 3.98 |
| Perla Aroma, private label (Whole beans, UTZ-certified, 500-gram package) | 
| 10.38 | |
| Douwe Egberts Aroma Rood (Ground coffee, 500-gram package) | 
| 11.98 |
Mid-range: Mid-range coffees are commercial coffees with a good and consistent quality profile, such as quality espresso. This segment typically consists of blends with a higher proportion of Arabica compared to the low-end segment. The mid-range segment represents a stable coffee market, in which sustainability certifications are important.
Mid-range coffees are often sold in supermarkets and by the food service industry. Premium private label ranges of retailers typically belong to the mid-range segment. Examples of mid-range products and prices, based on Albert Heijn’s retail prices in 2021, include:
| Product | Retail price (€/kg) | ||
| Mid-range | Lavazza Espresso Barista Perfetto (Whole bean, 100% Arabica, 500-gram package) | 
| 16.78 |
| L’Or Espresso Origin Brazil (Whole bean, 100% Arabica, UTZ-certified, 500-gram package) | 
| 16.98 | |
| Fairtrade Original Single origin Colombia (Whole bean, 100% Arabica, Fairtrade & organic-certified, 500-gram package) | 
| 17.78 |
High and upper ends: High-quality coffee mainly consists of washed Arabicas. These coffees are often single origin and coffees with a special story. The upper end of this segment consists of specialty coffees of excellent quality, often from micro or nano lots that go through processing methods such as naturals and honeys. These are mainly fully traceable and single origin Arabica beans with a cupping score of 85 and above. The high and upper-end segments are a small but growing market.
Sustainability certifications are more uncommon in this segment. This is because sustainability practices are often commonplace among buyers. Long-term contracts between suppliers and buyers characterise the high and upper-end segment, as well as higher prices. In addition, buyer and supplier usually agree on projects for communities and distribution of money to farmers, a common characteristic of certifications aimed at social impact. The high and upper-end segments do see a growth in organic-certified coffees, however.
Coffees from this segment are mainly sold directly by specialty roasters, at their physical and web shops as well as at coffee events. A recent trend is that some supermarkets have included a small offer of specialty coffees in their assortment. For instance, at the shelves of supermarket Albert Heijn you can find a range of organic specialty coffees from roaster Simon Lévelt. The organic supermarket Ekoplaza also offers specialty coffees of Simon Lévelt, as well as coffees from Dutch specialty roaster Bocca.
An example of a coffee event in the Netherlands is the Amsterdam Coffee Festival. An example of a specialised Dutch coffee web shop where you can find high and upper-end coffees is Dutch Coffee Dealer. To find examples of Dutch specialty roasters and cafés, refer to the European Coffee Trip website.
Examples of coffees in the upper-end market segments (based on Dutch Coffee Dealer’s prices in 2021) include:
| Product | Retail price (€/kg) | ||
| High and upper ends | Variety: Catimor, Caturra, Bourbon, Typica Process: Washed | 
| 42.00 |
Variety: Bourbon, Jackson Process: Fully washed | 
| 42.00 | |
Variety: Caturra Process: Natural | 
| 44.75 |
Value distribution: As the above examples show, end market prices for coffee vary depending on the targeted market segment. Green coffee export prices typically amount to only 5% to 25% of the end-market prices, depending on the coffee quality, the size of the lot and the supplier’s relationship with the buyer. Figure 4 below shows the value distribution of wholesale mainstream coffee. Roasters often end up taking more than 80% of the wholesale coffee price. A coffee farmer takes about 10%.
Prices for specialty coffee may have a reference on the international London and New York market prices but will command differentials. In the specialty segment, the shares of added value for farmers tend to be much higher than in the mainstream coffee market as well.
The Specialty Coffee Association provides an illustrative example of how exporters should look into their value chain, in terms of different costs and margins. Also refer to the Specialty Coffee Transaction Guide to get an idea of current market prices for specialty coffee. This guide quantifies anonymous contract and pricing data of importers and roasters, based on quality, quantity, and origin of purchased coffee.
Segmentation by type of consumption: In addition to the market segmentation by quality, the Dutch coffee market can also be segmented into in-home and out-of-home consumption:
- In-home consumption: About 70% of coffee consumption in the Netherlands takes place at home, with supermarkets as the main sales channels. Home consumption is becoming increasingly diverse because of different qualities and the growing popularity of coffee beans and capsules. The growing demand for beans and capsules has led to a decrease in the use of ground coffee, coffee pads and instant coffee. Despite this decline, filter coffee, coffee pads and instant coffee still register the highest sales volumes in Dutch supermarkets, with almost 73% of coffee sales in 2019. The COVID-19 pandemic has further driven up in-home consumption and the important role of retailers in coffee sales.
- Out-of-home consumption: About 30% of coffee consumption in the Netherlands occurs out-of-home. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, about 55% of out-of-home coffee consumption occurred at the office. Hotels, restaurants, and cafés make up 30% of the total out-of-home segment. Other important out-of-home segments include bakeries and coffees for take-away. In the Netherlands, coffee is the most popular consumed out-of-home drink with about 17% of total out-of-home consumption.
Figure 5: Dutch coffee market segmentation by in-home and out-of-home consumption
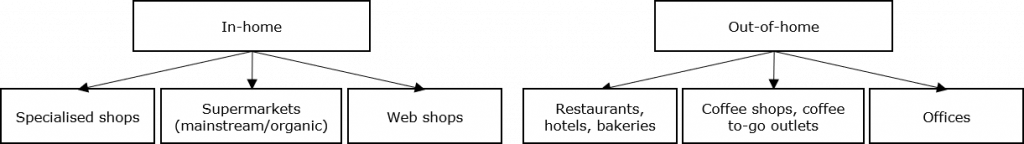
Source: ProFound
Tips:
- Compare the product assortment and price levels of Dutch supermarkets, such as Albert Heijn, with specialised stores, such as the Dutch web shop Dutch Coffee Dealer.
- Refer to our study on trends in the coffee market to learn more about developments within different market segments.
- Check the website of the Specialty Coffee Association (SCA) to learn more about the high-end coffee segment, market trends and main players.
Through what channels does coffee reach the end market?
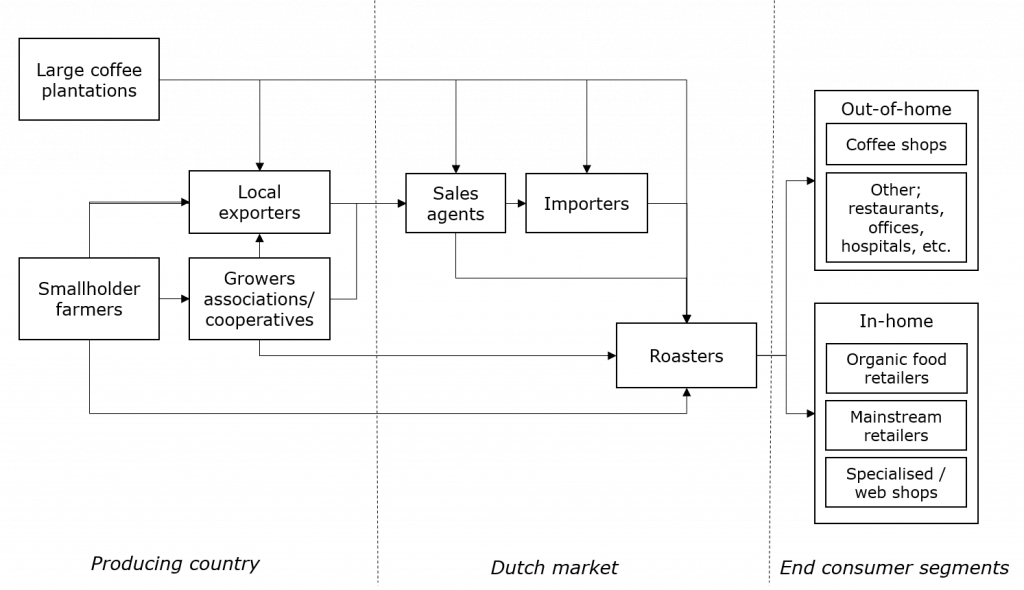
As an exporter, you can use different channels to bring your coffee onto the Dutch market. The way of entering the market will vary according to the quality of your coffee and your supplying capacity. Bear in mind that shortened supply chains are a general trend in Europe. This means that retailers and coffee roasting companies are increasingly sourcing their green coffee directly. The figure below shows the most important market entry channels for your green coffee beans in the Netherlands.
Figure 6: Market channels for green coffee in the Netherlands
Importers
Importers play a vital role in the coffee market, functioning as supply chain managers. They maintain wide portfolios from various origins, pre-finance operations, perform quality control, manage price fluctuations and establish contact between producers and roasters. In most cases, importers have long-standing relationships with their suppliers and customers. In general, importers either sell the green beans to roasting companies in the Netherlands or re-export them to other European buyers.
Large-scale importers usually have minimum volume requirements starting at around 10 containers, covering a wide range of qualities, varieties and certifications. At the same time, they provide strong support regarding logistics, marketing and financial operations. Examples of medium- and large-scale importers in the Netherlands include: J&B Commodity Trading, S&D Sucden, Greencof and Bijdendijk. These supply coffee to large roasters and mainstream retailers in Europe.
Specialised importers are able to buy small and mid-sized volumes of high-quality and single origin coffees, from microlots to full container loads (FCL). Examples of specialised importers in the Netherlands are: Daarnhouwer & Co, Trabocca, This Side up and The Coffee Quest. Coffees from these importers end up partly in mainstream retail, organic retail and specialty shops.
For whom is this an interesting entry channel? The most interesting channel for you will depend on the quality of your coffee and your supply capacity in terms of volume. If you are an exporter of green coffee beans and you can offer high volumes (10 containers or more), you should look into entering the Dutch market through large importing companies. These companies usually have agents or representative offices in producing countries, which can be your first point of contact.
Specialised traders can be interesting if you have evidence of high cupping scores of at least 80 or higher, although some buyers may require scores higher than 85, plus high transparency and traceability. Keep in mind that many specialised importers prefer to work directly with producers or cooperatives.
Large roasters
Most large roasters buy their own coffee beans from the country of origin, although they might also source through importers. Roasters usually perform analysis and cup testing to check the evenness of the roast and to identify any defects that can occur in post-harvest processes, such as fermentation, drying and storage. Large roasters usually blend different qualities of green coffees to safeguard quality consistency. The final product is distributed to retailers and the food service industry.
Roasters can operate under their own brands and/or private label. Examples of large roasters in the Netherlands include: Jacobs Douwe Egberts, Ahold Delhaize Coffee Company and UCC Coffee Benelux. An example of a medium-sized to large private label coffee roaster in the Netherlands is Pelican Rouge Coffee Roasters. Private label roasters may roast for mainstream clients as well as for specialty brands.
For whom is this an interesting entry channel? Supplying directly to large-scale roasters is only interesting if you are able to supply large volumes at consistent quality. If you work with bulk coffees, discuss minimum quality and other requirements, such as certification, with your potential buyer.
Medium-sized and small roasters
Although there is a growing number of small roasters which import green coffee directly from origin, the largest share of smaller roasters continues to buy their coffee via importers. This is the case as not all roasters can take on the additional responsibilities necessary to import directly from source. Importers help roasters with financial services, quality control and logistics. Nevertheless, small roasters often maintain a direct connection with their producers, as they need detailed information for storytelling to market the coffee to their clients (brands or consumers).
Small roasters are often specialised in single origins and the finest specialty coffees. Examples of small roasters in the Netherlands include: Boot Coffee, White Label Coffee, Back to Black, Bosbrand and Brandzaak. Refer to this website to find a long list of smaller Dutch coffee roasters.
Examples of medium-sized coffee roasters importing directly from origin are Mocca d’Or, Simon Lévelt and Peeze. Examples of medium-sized roasters engaged in private label are Neuteboom, Private Label Coffee and Beans Coffee Roasters.
For whom is this an interesting entry channel? Supplying to small roasters is interesting for producers and exporters that have high-quality coffees, micro lots, can guarantee traceability, and who are willing to engage in long-term partnerships. If you have very high-quality coffees and are currently working through an importer, for example, it would be interesting to explore direct trade possibilities to see whether you could connect directly with roasters. This requires you to have the financial means and technical know-how to organise export activities.
Supplying to medium-sized roasters may also be an interesting alternative if you have a consistent and reliable quality and volume. Most medium-sized roasters will also require one or more certifications for sustainable production. Be aware that many smaller roasters may not be importers, but that it is nevertheless important to interest them in your coffee. A logistic partner (importer) can then be found to ship your coffee to destination.
Intermediaries/agents
Agents act as intermediaries between you, coffee importers and roasters. These are actors with vast market knowledge and can help you assess and select interesting buyers. Some agents are independent, while others are hired to make purchases on behalf of a company. An example of an agent in Europe includes Eugen Atté (Germany).
For whom is this an interesting entry channel? If you have limited experience exporting to European countries, agents can play a very important role. Agents are also interesting if you have limited quantities of coffee or if you lack financial and logistical resources to carry out trade activities. Working with an agent is also useful if you need a trusted and reputable partner within the coffee sector. Be prepared to pay an extra commission for their work.
Tips:
- Find buyers that match your business philosophy and export capacities in terms of quality, volume and certifications. For more tips on finding the right buyer for you, see our study on finding buyers in Europe.
- Attend trade fairs and other events to meet potential Dutch buyers. Interesting events include SCA’s World of Coffee (every year in a different European city), Biofach (organic, Germany), COTECA (Germany) and the Amsterdam Coffee Festival. Attending such physical or virtual events can provide you with additional insight into the preferences of Dutch buyers and/or consumers, with regard to origin, flavour and sustainability certification.
- Check out the list of importers and roasters on the website of the Dutch Coffee and Tea Association. It will help you find potential partners and learn more about the Dutch market.
- Invest in long-term relationships. Whether you are working through importers or roasters, it is important to establish strategic and sustainable relationships with them. This will help you manage market risks, improve the quality of your product and reach a fair quality-price balance.
- See our study on buyer requirements for coffee to learn which European market standards and requirements you need to comply with when supplying to Europe.
- See our study on how to do business with European buyers for more information about complying with buyer requirements, how to send samples and how to draw up contracts.
3. What competition do you face on the Dutch coffee market?
In general, competition is higher for mainstream coffee with low added value. This segment is mainly dominated by major suppliers and cooperatives which are able to deliver large quantities so they can compete on price. It is difficult for small and medium-sized companies, for example those exporting a few containers per year, to compete in this segment.
In the specialty coffee market volumes are smaller, and the focus is more on quality, origin and sustainability. However, as demanded volumes are smaller, and more and more producers focus on this segment, competition can also be quite high. There are several competitions to identify the highest quality coffees produced worldwide, for instance the Cup of Excellence. These competitions might be an interesting entry point for this segment but entering this segment may require large investments.
New entrants to the market will face competition from already successful coffee exporters, especially due to their already established long-term relationships with buyers. Entering the market as a newcomer requires you to have extensive knowledge of your product assortment, stable quality and volumes, and good communication skills to start building your own new relationships with buyers. If the potential buyer is not yet operating in your country of origin, it might be more difficult to establish the first contact. You may be required to supply more extensive information about, amongst others, the producing regions, the producing communities and traceability.
Largest share of Dutch green coffee imports from Belgium
The Netherlands only sourced 36% of their coffee imports in 2020 directly from producing countries. The three main green coffee supplying countries to the Netherlands were Brazil, Vietnam and Colombia. The largest share of imports was supplied by neighbouring European countries. The Netherlands is geographically located between the two largest coffee ports in Europe: Antwerp (Belgium) and Hamburg (Germany). This explains why 58% of all Dutch imports were supplied by Belgium, and 4.9% of total imports by Germany.
Brazil: the world’s largest coffee producer
Brazil is the world’s largest coffee producer, with production volumes amounting to 3.63 million tonnes between July 2019 and June 2020. Brazil produces both Arabica (75%) and Robusta (25%), but about 80% of exports are Arabica. In 2020, the Netherlands imported about 29,000 tonnes of green coffee directly from Brazil, 16% of total Dutch imports. Between 2016 and 2020, Brazil consolidated its position as a leading direct supplier to the Netherlands, with an average annual growth rate of 11%.
Brazil’s coffee-producing areas are relatively flat, which has intensified the use of mechanical pickers in the industry. This has drastically reduced labour costs in Brazil’s coffee production, but also resulted in lower quality, as machines do not distinguish between ripe and unripe cherries. Coffee prices in Brazil went down, especially in relation to other coffee producing countries. Brazil mostly produces natural and pulped natural coffees. Low-grade Brazilian Arabica is mostly used in blends.
Although the country is mainly known for exporting large volumes of standard quality, the country also has a strong reputation as a producer of specialty coffees. This is in part thanks to the Brazil Specialty Coffee Association, which aims to elevate the quality standards and enhance value in the production and marketing of Brazilian coffees. Examples of successful exporters of specialty coffees in Brazil are Burgeon and Bourbon Specialty Coffees. Large Brazilian exporter Costa Café has also started exporting specialty coffees in addition to its regular mainstream coffee exports.
Vietnam: the world’s largest Robusta supplier
Vietnam is the world’s second-largest coffee producer, with production volumes reaching 1.878 million tonnes between October 2019 and September 2020. Approximately 96% of Vietnamese coffee production consisted of Robusta coffees. The Netherlands imported about 9,500 tonnes directly from Vietnam in 2020. Between 2016 and 2020, Vietnamese exports to the Netherlands increased at an average annual rate of 5.4%.
Vietnam’s coffee production is strongly focused on creating large volumes of standard quality coffees, mostly directed at the instant coffee market. In recent years, Vietnam’s Robusta exports have been faced by strong competition from the Brazilian Conilon and Robusta beans from other countries, leading to slightly lower exports. Examples of large Vietnamese coffee exporter groups include Simexco Daklak, Intimex Group, Tin Nghia Corporation and Mascopex.
It is likely that trade between the European Union and Vietnam will increase again in the near future, as the European Union-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA) entered into force in August 2020. This removed tariffs on all green, roasted and processed coffee from Vietnam.
To help boost increased coffee trade through the EVFTA, the Vietnamese government requested the country’s coffee industry players to apply advanced cultivation, processing and storage technologies, to increasingly meet buyer requirements from European importers.
In addition, government efforts have been more and more directed towards improving the quality of coffee beans. As there is an increasing interest in high-quality coffees on consumer markets, Vietnam’s specialty coffee industry is slowly developing. An example of a successful exporter of Vietnamese specialty coffee is Blue Son La.
As climate change poses a serious threat to the Vietnamese coffee sector, the country is working hard to achieve greater coffee sustainability. In collaboration with many international actors, such as Bioversity and CIAT and IDH, private and public actors in Vietnam increasingly focus on making coffee production in the country a sustainable practice and source of income for smallholder farmers.
Colombia: the largest supplier of washed Arabicas
Colombia is the world’s third-largest coffee producer, with production volumes amounting to 846,000 tonnes between October 2019 and September 2020. The Netherlands imported 6,200 tonnes of green coffee directly from Colombia in 2020. Between 2016 and 2020, Dutch imports from Colombia increased at an average annual rate of 20%. In general, coffee production in Colombia has been favourable in 2020 due to the highly successful replanting program of coffee rust-resistant varieties in the past years.
Colombia is the world’s largest producer of washed Arabica. The Colombian Coffee Growers Federation strategically promotes and markets Colombian coffee, solidifying the country’s established image and brand for high-quality coffees. The Café de Colombia trademark is a registered protected geographical indication (PGI) in Europe, which is unique among coffee-producing countries.
Colombia is an important producer of certified coffees worldwide. Colombia is the second-largest producer of Rainforest Alliance-certified coffees and the largest producer of Fairtrade-certified coffees. The wide availability of certified coffees has allowed green coffee exporters to access various markets and segments in Europe. Examples of successful Colombian cooperatives or private organisations exporting coffee to the international market include InConexus, Red Ecolsierra, La Maseta and Cadefihuila.
Honduras: large supplier of organic coffee
Honduras is the world’s sixth-largest coffee producer at 324,000 tonnes between October 2019 and September 2020. The Netherlands imported about 3,800 tonnes of green Arabica coffee from Honduras in 2020. Between 2016 and 2020, supplies from Honduras decreased at an average annual rate of -3.3%.
The Honduran Coffee Institute IHCAFE has been promoting the production of value-added coffees, either through certification or by actively improving coffee quality. The country has grouped coffee production and quality specifications into six different regions according to differences in microclimates and soil composition. Honduran exports of specialty organic coffees increased by 30% between 2016 and 2017 because of these efforts.
In addition to the growing reputation as a high-quality coffee supplier, a relatively large share of Honduras’ coffee supplies is organic. In 2019, about 24,000 hectares were dedicated to organic coffee farming in Honduras, approximately 5.4% of the total Honduran coffee area. This relatively low share underlines the existing growth potential of Honduras as an organic producer. Nevertheless, with 37,000 tonnes or 26% of European organic coffee imports in 2019, Honduras was already the second-largest supplier of organic coffees to the EU, only after Peru.
Examples of successful exporters in Honduras are Asoprosan, Cafico, Capiro Coffee Export and Aruco.
China: on its way to consolidating its position as a specialty coffee producer
In 2020, Chinese exports to the Netherlands reached 2,300 tonnes of green coffee. Between 2016 and 2020, green coffee imports from China to the Netherlands increased at an average annual rate of almost 48%.
China is the thirteenth-largest coffee producer in the world. Between October 2019 and September 2020 China produced 114,000 tonnes of green coffee, of which all was Arabica. About 90% of all coffee produced in China is fully washed.
The increase in quality and sustainable farming practices has boosted the importance of China as a coffee-supplying country. Since the early 2000s production has gone up considerably, and more and more large multinational coffee traders have opened coffee offices in the country. For instance, coffee trader Sucafina recently opened its office in China in 2020.
However, China still faces some challenges in coffee production, such as the lack of infrastructure that limits growing capacity, and generally outdated and ineffective processing equipment that might hinder quality improvements. As an answer to these challenges and the rise in coffee demand globally, the Chinese government focuses on increasing national production. Also, both public and private entities are focused on boosting the specialty coffee production in China. For instance, the Coffee Quality Institute is working in China to improve coffee quality from the production level and to optimise processing practices, amongst others.
Tips:
- Identify your potential competitors. To be successful as an exporter, it is important to learn from them too. Look into their marketing strategies, the product characteristics they highlight, and their value addition approaches. Successful companies that already export to the European market from which you can learn include, for example, Indian Organic Farmers Producer Company (India), ACPU (Uganda), O’Coffee (Brazil), Bourbon Specialty Coffees (Brazil) and La Meseta (Colombia). Another interesting exporting company to learn from is Caravela Coffee, which has a wide portfolio of specialty coffees from Latin America, facilitates contact between roasters and producers, and has set up representative offices in destination markets.
- Identify and promote your unique selling points. Give detailed information about your coffee-growing region or origin, the varieties, qualities, post-harvesting techniques and certification of the coffee you offer. You can also tell the history of your organisation, your coffee growing farm and the passion and dedication of the people working there. These are all elements that make your company unique.
- Actively promote your company on your website and trade fairs. Quality competitions also provide good opportunities to share your story. For instance, refer to the auctions organised by the Cup of Excellence.
- Are you interested in exporting high-quality coffee? Learn more about cupping scores on the website of the Specialty Coffee Association (SCA). You can also consider getting a Q Arabica or Q Robusta Grader certificate to be able to cup and score your coffee through smell and taste according to international standards.
- Work with other coffee producers and exporters in your region if your company size or product volume are too small. As a group, you can promote good-quality coffee from your region and be more attractive and more competitive on the European market.
- Develop long-term partnerships with your buyers. This implies always complying with their requirements and keeping your promises. This will give you a competitive advantage, more knowledge and stability on the Dutch market. See our tips on doing business with European coffee buyers for more information.
ProFound – Advisers In Development carried out this study on behalf of CBI.
Please review our market information disclaimer.
Search
Enter search terms to find market research