
Entering the European market for gums
To enter the European gums market you must meet the European Union’s (EU) mandatory requirements. At the same time, you should meet common additional requirements for niche markets. This is necessary for you to enter the European market.
Contents of this page
Gums have a wide range of applications in several food sectors, but the European gums market can be divided into three main segments, each having different channels for you to enter. You face competition from suppliers in other developing countries, companies, and competing products in the European market. For gum arabic, most competition comes from the gum belt. The majority of Guar gum comes from India and Pakistan.
1. What requirements and certifications must gums comply with to be allowed on the European market?
What are mandatory requirements?
EU mandatory requirements
You must ensure your product is safe for the European market. You must therefore comply with the European Union’s mandatory requirements for natural food additives. Failure to do so will prevent your guar gum or gum arabic from being sold in the European market. To enter the European market, you must comply with a number of EU regulations meant to guarantee food safety, such as:
- The General Food Law, which ensures your guar gum or gum arabic’s safety.
- Regulation (EC) 852/2004, which requires a Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system in place, if you are a food processor of guar gum or gum arabic.
Tips:
- Read the CBI study on the requirements for natural food additives to be allowed in the European market, which provides further information about mandatory requirements to entering the European market.
- Read the EU’s guidance on how to be compliant and implement the EU’s General Food Law. This will give you a greater understanding of a major mandatory requirement for you to comply with to enter the European market.
- Read the EU’s factsheet on food traceability, which provides useful information about food traceability in the EU.
- Read and comply with the EU’s Key Obligations of Business Operators.
Contamination
The EU legally requires proof that your guar gum and gum arabic is not contaminated with or contains a maximum level established for elements in three categories:
- Physical –plastic, metal and dirt residues
- Chemical – pesticides
- Biological – bacteria
You must prove your guar gum or gum arabic is free from contaminants in these three categories, or that it is within the levels set by the EU. Failure to comply prevents your product from entering the European market. Exporters of guar gum in India specifically must comply with EU Regulation 2015/175, which lays down special conditions applicable to the import of guar gum originating from India due to contamination risks by pentachlorophenol and dioxins.
The EU has set maximum residue levels (MRLs) for pesticides (EC Regulation 396/2005) and heavy metals (EC Regulation 1881/2006). You must ensure your guar gum or gum arabic does not contain pesticides nor heavy metals above the levels set by the EU. Failure to comply with the MRLs prohibits your gum from being sold in the European market.
European buyers routinely test imported guar gum and gum arabic to check that it is not contaminated and respects MRLs, which is yet another reason for you to comply with these requirements.
Tips:
- Use the EU’s MRL database to identify the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for guar gum and gum arabic.
- Visit the European Union’s Export Helpdesk for further information about MRLs.
- Consider utilising guidance provided by the Integrated Pest Management system on reducing pesticide use in guar gum and gum arabic production.
Minimum quality levels for gums
The EU has set mandatory minimum quality levels for guar gum and gum arabic to enter the European market in EU Regulation 231/2012, which concerns guar gum and gum arabic’s synonyms, definition, description, identification, purity and microbiological criteria.
- Guar gums minimum quality levels are found on pages 144 of EU Regulation 231/2012 under E412 GUAR GUM.
- Gum arabic’s minimum quality levels are available on pages 145 and 146 of EU Regulation 231/2012 under E414 ACACIA GUM, another common name for gum arabic.
You must comply with the EU’s minimum quality levels for guar gum and gum arabic to enter the European market.
Tip:
- Comply with the mandatory minimum quality levels for guar gum and gum arabic as outlined in EU Regulation 231/2012.
Nutritional claims
Soluble dietary fibres, which are indigestible parts of gums are found in guar gum and gum arabic. European consumers are seeking functional foods with health benefits, some believe soluble fibres are good for their health. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not approved any health claims related to dietary fibres. European food manufacturers are therefore not allowed to make health claims concerning soluble dietary fibre when promoting their products to consumers. Thus, you must not make any claims concerning soluble dietary content in guar gum nor in gum arabic.
Regulation (EC) 1924/2006 Annex lists the only nutritional claim you are allowed to make concerning guar gum and gum arabic’s high fibre content. Thus, as an exporter of guar gum or gum arabic you can only make this nutrition claim:
- Source of fibre: A claim that a food is a source of fibre, and any claim likely to have the same meaning for the consumer, may only be made where the product contains at least 3g of fibre per 100g or at least 1.5g of fibre per 100 kcal.
- High in fibre: A claim that a food is high in fibre, and any claim likely to have the same meaning for the consumer, may only be made where the product contains at least 6g of fibre per 100g or at least 3g of fibre per 100 kcal.
When guar gum or gum arabic is used in foods for their thickening, stabilising and emulsifying functionalities, they are used in concentrations below 1%. However, guar gum and gum arabic gum can also be used in larger concentrations in functional foods.
Tips:
- Routinely check the EU’s Register of Nutrition and Health Claims for updates and ensure you do not make any claims that you are not allowed to make.
- Include information about guar gum or gum arabic’s high fibre content in your marketing materials, since it is one of their key strengths.
Labelling and packaging requirements
The EU’s Classification, Labelling and Packaging (CLP) Regulation (EC Regulation 1272/2008) identifies hazardous chemicals and informs users about their hazards through standard symbols and phrases. To enter the European market, your guar gum or gum arabic must comply with the EU’s CLP regulation. Failure to do so will prevent it from entering the European market.
In addition, the EU legally requires the corresponding warning labels to be applied on special packaging used. You are legally required to use the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) to do this. You must therefore use the GHS’s labels on your guar gum or gum arabic’s packaging.
Figure 1: Hazard labels for guar gum – harmful symbol
Figure 2: Hazard labels for gum arabic - Health hazard and harmful symbol
Guar gum and gum arabic must comply with EU legislation on labelling of food additives and flavourings to enter the European market. As an exporter, your guar gum or gum arabic will have to comply with different requirements depending on whether or not it is intended for sale to the final consumer. You must comply with the labelling requirements outlined in Chapter IV – LABELLING under Articles 21, 22 and 23 of Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 and Regulation (EC) No 1334/2008.
EU organic certified products must meet certain labelling requirements. If you export organic certified guar gum or gum arabic, you must comply with EU organic labelling requirements, including displaying the code number of the certification authority along with where the agricultural raw materials composing the product have been farmed next to the EU organic logo.
Tip:
- Review the European Chemicals Agency’s (ECHA) guidance on CLP regulation to learn more about labelling requirements.
Documentation
European buyers of gum arabic value exporters that can provide organised and well-structured product and company documentation, so make sure that you can provide them to European buyers. Doing so is likely to increase your chances of entering and trading in the European market. In addition, it also creates business credibility, since it makes you look organised and well prepared.
Exporters of guar gum and gum arabic are generally expected to provide European buyers with:
- Safety data sheets (SDS)
- Technical data sheets (TDS)
- Certification of analysis (COA)
Figure 3: Technical Documentation Descriptions
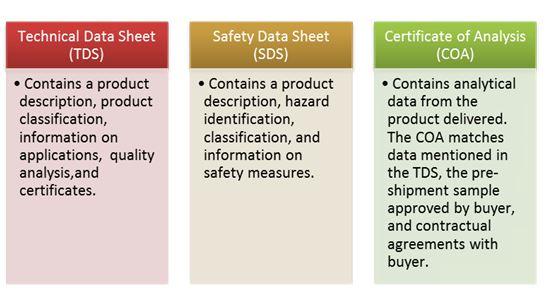
Source: Ecovia Intelligence
You should consider having SDS, TDS and COA for your guar gum or gum arabic ready for European buyers. Informing potential European buyers that you already have them is likely to increase your chances of entering the European market.
Tip:
- Review this sample safety data sheet (SDS) and certificate of analysis (COA) for gum arabic.
Convention on Biological Diversity, Access and Benefit-Sharing
The scheme of the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit-Sharing (ABS) of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) aims to ensure the benefits of genetic resources and long-established knowledge are shared fairly. This is particularly important for ingredients collected from the wild.
The EU has adopted international treaties and protocols on using plant resources into European law, including CBD. It is probable that CBD is also a part of your country’s national laws. If your country is a signatory of the Nagoya Protocol, you must meet comply with it. Failure to comply results in your guar gum or gum arabic being prohibited from entering the European market.
Tips:
- Visit the CBD website which provides a range of useful information on CBD and ABS. Their handy country function tool provides useful information specific to your country.
What additional requirements do buyers often have?
Quality and consistency requirements
European buyers demand 100% pure and natural guar gum and gum arabic. You have to make sure your guar gum or gum arabic is not mixed with any other gums that have similar characteristics, and is unadulterated by the addition of any chemicals.
European buyers usually have a preference for lightly coloured guar gum and gum arabic with a minimal smell so as not to affect the appearance of manufactured food and drinks. Interviews with European buyers revealed their general preference for purchasing guar gum and gum arabic with a viscosity level of 3,500 and 5,000 respectively, which are the most popular in the European food industry. Thus, consider meeting the preferences of European buyers to increase your chances of doing business with them.
European buyers also usually analyse gum arabic composition for adulteration. To verify quality at origin, the Sudanese Standards and Metrology Organization developed a gum arabic standard, which Sudanese exporters of gum arabic should consider meeting.
Consumers demand good quality food and drink products. Thus, European buyers of guar gum and gum arabic want a consistent quality ingredient because it is essential to the manufacturing of good-quality food and drink products. European buyers prefer a standardised quality product across all packaging sizes per order volume.
Tips:
- Find out if European buyers have specific quality requirements for guar gum and gum arabic, and consider meeting them. This is because there are various levels of quality and processing of gums, specifically gum arabic. European buyers may supply a wide range of costumers that have specific requirements for gums.
- Review and consider meeting the Association for International Promotion of Gums (AIPG) Good Practices for Gums guidance. Doing so is likely to increase the quality of your gum arabic, thus increasing your chances of entering the European market.
Quality management standards
European buyers of natural ingredients for food additives are increasingly using quality management standards when assessing the credibility of prospective exporters. Adopting quality management standards gives you credibility because it shows your commitment to delivering high-quality ingredients and gives your company a favourable image. Adopting quality management standards can also help to show your compliance with mandatory requirements.
You should therefore consider adopting quality management standards as it increases the quality of your gums, and makes you more appealing to buyers.
Consider adopting quality standards concerning production methods. Examples of quality standards that you can adopt are International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 22000 and ISO 9001:2015, as well as Food Safety System Certification (FSSC) 22000. You should also consider following the guidelines outlined in Hazard Analysis & Critical Control Points. Other examples include British Retail Consortium Global Standard for Food Safety (BRCGS) and International Featured Standards (IFS) certification.
Tip:
- Inform European buyers of the standards you meet and display them on your website and marketing materials because it gives you an advantage as buyers look at standards when assessing exporters.
Labelling and packaging
Consider meeting common additional labelling and packaging requirements European buyers of guar gum and gum arabic have. The following should be listed on your product documentation and labels in English unless asked otherwise:
- Name and address of exporter;
- Product name – for example, organic guar gum;
- Batch number – which allows product traceability;
- Whether the product is for use in food products, for example, if it is food grade;
- Place of origin – for example, India, Pakistan, Sudan and Chad;
- Date of manufacture;
- Best-before date – time after which a product may begin to lose its properties, for example flavour and texture;
- Net weight in metric units;
- Recommended storage conditions – which helps to ensure the product retains the highest quality.
European buyers want high-quality guar gum and gum arabic, thus you need to preserve its quality by using appropriate packaging materials. You should use plastic (polypropylene) bags with a plastic (polyethylene) lining in your guar gum or gum arabic’s inner packaging, with a kraft paper bag for its outer packaging. Guar gum and gum arabic attract moisture, so they need to be packaged in waterproof materials. Failure to do so is likely to result in quality deterioration, discouraging European buyers to accept it.
Tips:
- Contact European buyers to ask them if they have specific labelling and packaging requirements in addition to the mandatory requirements. Meeting these additional requirements, if they exist, will help you access the European market.
- Consider recycling or re-using packaging materials, for example kraft paper bags. Environmental sustainability is becoming increasingly important for European buyers.
- Ensure certified organic and conventional are separated physically to prevent contamination.
Payment terms
Payment is central to all trade, presenting risks to all involved. You should therefore do risk assessments of available payment terms before starting a trading relationship with European buyers of guar gum and gum arabic. You should work towards reducing your risks as an exporter while working towards meeting the needs of European buyers.
Several methods of payment are available for exporters to choose from. However, letters of credit (LC) are considered to be the safest payment method for both exporters and importers. This is because they allow both parties to contact an unbiased adjudicator to settle any issues, usually a bank. The chosen bank is a guarantor of full payment for exporters, as long as goods have been dispatched. In these situations, to prevent additional losses, exporters should pay for the return of goods dispatched and find new buyers for them.
Depending on their needs, exporters and importers can choose from a number of LC payment terms. They include standby, revocable, irrevocable, revolving, transferable, un-transferable, back to back, red clause, green clause and export/import. Standby is considered to be the safest for exporters, routinely being used in international trade as it provides security to both exporters and importers who have little trading experience together. Cash in advance, documentary collections and open account are other payment terms available.
Figure 4: Payment risk diagram
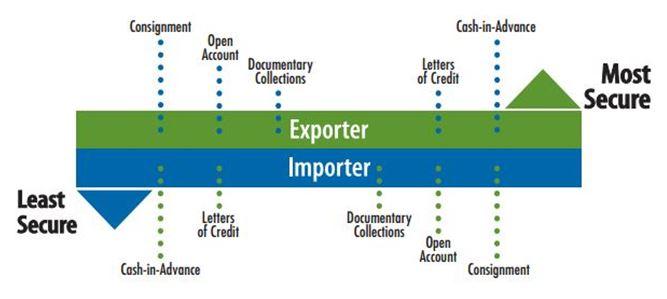
Source: trade.gov
Tips:
- You should work towards reducing your risks and meeting the needs of European buyers to avoid financial and business losses.
- Be open minded, flexible and remember there will be tensions and trade-offs with buyers, especially if it is your first time doing business with them.
- See the CBI study on organising your natural food additives exports to Europe, which provides useful guidance on available payment terms used in this sector.
Delivery terms
You should carefully consider time, volume and cost, the three key factors of delivery, when agreeing delivery terms with European buyers of guar gum and gum arabic. Failure to meet agreed delivery terms with buyers may end your trading relationship with them. As an exporter, you should carefully consider the following with regard to the three key factors:
- Delivery time – European buyers prefer shorter delivery times . Air freight is more reliable in terms of on-time delivery, and also generally faster than sea freight. It is important to note delivery times may be longer due to the COVID-19 pandemic, including because different measures and restrictions affect the movement of goods. For example, Sudanese exporters of gum arabic have reported local lockdowns in the port of Sudan causing longer delivery times.
- Delivery volume and order quantity– Larger volumes are often cheaper to transport via sea by ship. Meanwhile, as margins get lower, air freight can be less expensive to transport smaller volumes.
- Cost of delivery method – For larger volumes, air freight is generally 4–6 times more expensive than sea freight. If you increase volumes, it is unlikely prices of transporting your freight will increase significantly. Note, due to the global COVID-19 crisis, the cost of air freight has been increasing. However, freight costs started to normalise in 2021.
Figure 5: Incoterms
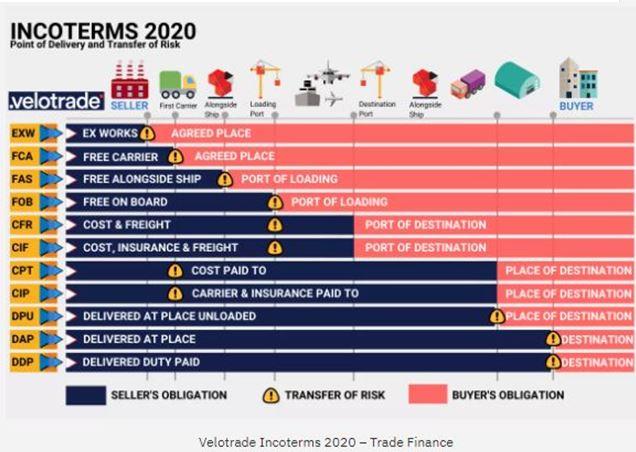
Source: velotrade.com
Tips:
- Keep in mind the three key factors of delivery — time, volume and cost — when deciding which delivery terms are the most suitable for your needs.
- Speak to your logistics provider about what COVID-19 means for you before agreeing delivery terms with European buyers.
- Be open minded, flexible and remember there will be tensions and trade-offs with European buyers, particularly if it is your first time doing business with them.
2. What are requirements for niche markets?
Organic certification
There is growing consumer demand for organic products in Europe. Ecovia Intelligence expects the European market for organic food and drink to continue to grow in the coming years, generating strong demand for certified organic food ingredients.
You should consider getting organic certification for your guar gum and gum arabic to increase your chances of accessing the European market. Organic certification demonstrates the product meets a certain quality standard. It also allows you to use certification as a selling point when approaching prospective European buyers. For guar gum and gum arabic to be traded as organic on the European market it must comply with EU organic regulation.
After obtaining organic certification, European buyers often request a certificate of inspection (COI), a mandatory EU requirement for any organic ingredient traded on the European market. You must therefore have a COI for your organic guar gum or gum arabic.
Tips:
- Ensure you have a certificate of inspection (COI) that is up to date to with the latest EU changes that came into force on 3 February 2020.
- Inform buyers you have organic certification when approaching them to increase your chances of entering the European market.
- Visit the IFOAM website which provides useful information on EU organic certification.
Environmental and social sustainability
There is growing consumer demand for products that follow environmental and social responsibility standards in Europe, a trend that is set to continue. For example, there is growing consumer demand for ethically produced products, which grew 18.3% in the last five years.
Consider producing your guar gum and gum arabic according to environmental and social standards to increase your chances of entering the European market. With regard to environmental sustainability, consider meeting the UNCTAD BioTrade Principles and FairWild Standards. To prove you meet social responsibility standards, considering getting FLO Fairtrade certification or meeting FairForLife standards.
Tip:
- Use certification status you have obtained to your advantage. For example, make your product more appealing to European buyers by informing them that you have the certification along with using it in your marketing materials.
3. Through what channels can you get gums on the European market?
Gums are used by the food industry, pharmaceutical industry and personal care industry in the European market. However, this study only focuses on the use of guar gum and gum arabic in the food industry.
Guar gum is used in the food industry, which can be sub-segmented into the beverages, confectionary, meat, bakery, dairy and condiments. Guar gum is also used in the pharmaceutical, personal care and fracking (a technique designed to recover gas and oil from shale rock) segments.
Gum arabic is used in the food industry, which can be sub-segmented into beverages, confectionary, bakery, dairy, functional foods and flavourings. Gum arabic is also used in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, printing and paper-making industries.
How is the end market segmented?
This study focuses on the use of gum arabic and guar gum in the food industry. Food industry sub-segments for these gums include beverages, confectionary, meats, bakery, dairy, flavourings, functional foods and condiments.
Other end-user industries for guar gum are the pharmaceutical, personal care and fracking industries. The cosmetics and printing industries are other end-user segments for gum arabic. Figure 6 shows examples of gum products in the European market.
Figure 6: End-user market segments for gums

Source: Various
Food industry
The global guar gum market is estimated to reach US$824.28 million in 2021, and US$1.2 billion in 2026. Demand for food-grade guar gum is predicted to grow in line with a growing food processing industry. Meanwhile, the global gum arabic market was valued at US$ 250 million in 2020. The market is forecast to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 3.1 percent until 2027. Gum arabic’s use in the food and beverage industry is a key driver behind this growth. An estimated two thirds of gums, including gum arabic and guar gum, is used in the food and beverage industry.
Guar gum is used in beverages for its thickening and viscosity control, solubility in cold water, resistance to breakdown under low pH conditions. It is also present in beverages because of its ability to improve mouth feel and shelf-life. Gum arabic is used in a wide range of beverages, ranging from carbonated soft drinks to alcoholic beverages. It can be used as an emulsifier, stabiliser, for fibre enrichment, and as a suspending agent in flavours and soft drinks, smoothies, clarified or cloudy juices. Gum arabic’s application in beverages accounted for the largest share of 32.2% of the global market in 2018.
Guar gum is used in confectionary due its properties of viscosity control, moisture retention, bloom control, gel creation, agar and gelatine replacer, glazing agent. The confectionery products segment accounted for one of the largest shares of the global guar gum market in 2017. Gum arabic is used in confectionary because it prevents sugar crystallisation, along with its function as a texturising, whipping, gelling, coating, fat and sugar separating, barrier and film-binding agent. It is also used for fibre enrichment. In low-calorie candies, gum arabic is used to compensate for the loss of texture, mouthfeel and body resulting from the replacement of sugars with artificial sweeteners.
Guar gum has strong water-holding capacity in both hot and cold water, so it is used as a binder and lubricant in the manufacture of sausage products and stuffed meat products. Guar gum is also used for specific functions it performs in processed meat products, including syneresis control, prevention of fat migration during storage, viscosity control of liquid phase during processing, cooling and control of accumulation of water in cans during storage.
Guar gum is used in bakery as a moisture retention agent and as a dough conditioner along with its desirable binding and film forming properties that retard the penetration of fats and oils. Bakery products account for one of the largest shares of the global guar gum market. Gum arabic is used in bakery products for smoothness, crispness, moisture stabilisation, shelf-life extension, fibre enrichment, food protection and fat reduction. Gum arabic is also used for its nutritional benefits, such as GI reduction.
Guar gum is mainly used in frozen dairy products because it provides stabilisation, particularly in ice cream products, where it also improves body, texture, chewiness and heat shock resistance. In dairy products, gum arabic is used as an emulsifier, binder, stabiliser, thickener, as a suspending agent and for fibre enrichment. Gum arabic is also used for fat reduction and to improve mouthfeel.
Guar gum is used in condiments because of its ability to improve free flowing properties of sauce and reduce separation between water and oil phases. Guar gums cold water solubility and high acidic emulsions enable it to be used as a thickener in salad dressings, as well as in pickle and relish sauces.
Gum arabic is also used as an emulsifier, flavour stabiliser and encapsulating agent. Gum arabic is used in functional foods for fibre, vitamins and mineral fortification.
Most of the high-grade processing of gum arabic takes place in Western Europe and in the US. Producers of standardised grades of spray-tried and granulated gums, and those producing customised gum arabic specific to their client specifications are the most popular in Europe. Processes include making uniform pebble-size pieces, granulating, powdering and spray-drying. Around half of the use of gum arabic is in sun-dried form; a third is in crude form, particularly for confectionery applications with powdered and granulated grades, along with some siftings making up the balance.
Quality and consistency are important to European buyers of guar gum and gum arabic. European buyers have revealed a general preference for buying guar gum and gum arabic with a viscosity level of 3,500 and 5,000 respectively, the most popular in the European food industry. You should therefore consider meeting the preferences of European buyers to increase your chances of doing business.
Pharmaceuticals industry
Guar gum is widely used in the pharmaceuticals industry as a gelling, thickening and emulsification agent, in the stabilisation of active ingredients, water retention and water phase control, process aid additive and as a modifier of flow characteristics in solution.
Gum arabic is used in the pharmaceuticals industry to control viscosity, improve density, suspend insoluble drugs and prevent the precipitation of heavy metals from solutions. It is also used as an emulsifying agent, an adhesive or binder for pharmaceutical tablets, a masking agent for acrid tasting substances, and a demulcent in cough syrups.
Personal care industry
Guar gum is used in the personal care sector as an emulsifier, stabiliser, thickener, moisturiser, softener, conditioner and whitening agent. Gum arabic is used in a range of personal care products as an emulsifying, stabilising, binding, film-forming and protective agent, as well as a foam stabiliser, thickener and adhesive.
Other industries
Due to its dispensability and thickening properties, guar gum is also used in the fracking industry. Gum arabic is used in the printing industry as a base for photosensitive chemicals, as a component of solutions used to increase hydrophilicity and impart ink-repellence to metal plates, and as a protective coating to prevent plate oxidation.
Specific requirements for gums by the pharmaceutical, personal care and other industries include the level of processing, which is dependent on the end user application per industry, such as a in a finished product like medicinal tablets in the pharmaceutical industry.
Tips:
- See the CBI study on which trends offer opportunities or pose threats in the European natural food additives market for useful information about the European natural food additives market.
- Visit trade fairs to test if the industry is open to your product, get market information, and find potential buyers. They will also give you the chance to speak to end-users, importers, processors and gauge your competition, especially how they are marketing their products.
- See the CBI study on tips for finding buyers in the European natural food additives market for an overview of trade fairs in this sector.
Through what channels do gums end up on the end-market?
Figure 7 shows the export value chain for guar gum and gum arabic en route to the European market.
Figure 7: Export value chain for guar gum and gum arabic
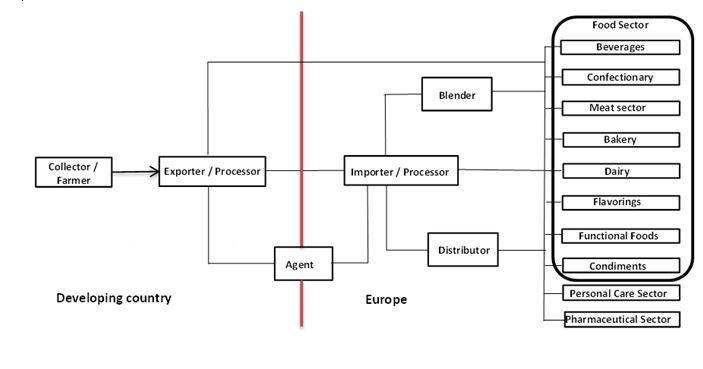
Source: Ecovia Intelligence
Importers and processors
European importers are one of your main entry points to the European market. Their expertise in the global sourcing of natural ingredients ensures quality, documentary and regulatory compliance for buyers, such as processors, blenders and food manufacturers. Importers of guar gum in the European market include Jebsen & Jessen Life Science GmbH, Altaquimica and Beckmann-Kenko.
European importers and processors are also one of the main entry points to the European market. European processors further process gum arabic in Europe because developing countries are generally unable to meet quality requirements demanded by European food manufacturers because they lack processing facilities and technical expertise, according to European processors. Nexira is the leading importer and processor of gum arabic in Europe. Most processed gum arabic is exported from France to other European countries and overseas. Alland & Robert is another leading importer and processor of gum arabic.
Agents
An export agent is a firm or an individual that undertakes most of the exporting activities on behalf of an exporter, usually charging a commission. Agents can be found in developing countries and Europe. However, it is uncommon for companies to use agents in the European market. You could work with agents who represent and act on your behalf in the European market.
Other channels
The processing and exporting of guar gum or gum arabic as an ingredient can be concentrated in one company in the country of origin, such as Supreme Gums Pvt. Ltd., an established Indian company exporting guar gum to the European market.
Tip:
- Be prepared to send high-quality samples to prospective buyers who will test samples to assess whether you are a credible supplier of guar gum or gum arabic. It is standard procedure to request samples in the food industry. Being prepared gives you an advantage when you are looking to access the European market
What is the most interesting channel for you?
For exporters of guar gum, importers with a large market share in the beverage sector are the most interesting channel because of their expertise in importing and distributing guar gum in the European market, their good understanding of the European natural food additive market, and their wide range of customers. Nexira is a major European importer of gum arabic, which has applications for its gum arabic in sectors such as the European beverage sector. Nexira has a 40% market share of the global gum arabic market. European importers also have storage facilities and established logistics networks.
For exporters of gum arabic in a developing country, European processors are the most interesting channel for you. They further process gum arabic to the standards demanded by European food companies. Alland & Robert is another large processor of gum arabic in the European market.
Tip:
- See the CBI study on tips for finding buyers in the European natural food additives market for useful information and guidance on finding buyers in the channels you can use to enter the European market, particularly importers and processors, your main points of entry.
4. What competition do you face on the European gum market?
Which countries are you competing with?
Successful developing countries exporting guar gum and gum arabic to the European market often pool the key strengths that are important to their success, including improved infrastructure, governmental support and favourable climatic conditions. As to gum arabic, a key strength shared by Sudan, Chad and Nigeria is that they are based in the ‘gum belt’, where acacia trees grow, and from which gum arabic gum is extracted.
India
Eurostat Data from 2020 showed India was the largest exporter of guar gum to Europe in terms of volume. India has a well-established commercial guar gum production industry which accounts for approximately 80% of global production; this is one of India’s key strengths. The rain pattern of monsoons in northern parts of India provides ideal conditions for guar gum cultivation, yet another of India’s key strengths. However, a key challenge facing India’s guar gum industry concerns adverse climatic conditions affecting crop production, yields and prices, such as excessive rainfall during the monsoon.
Challenges facing small to medium-sized Indian enterprises include community processing systems being absent with most processing done by private processors; producer income being low due to many intermediaries; and high involvement of speculators who control the trade. European buyers of Indian guar gum perceive India positively. According to their feedback, Indian exporters provide good-quality products, good prices, and are reliable
Pakistan
Eurostat data shows Pakistan was the second-largest exporter of guar gum to Europe in 2020 in terms of volume. Pakistan has an established commercial guar gum production industry which accounts for 15% of global production, one of the country’s key strengths. And just like India, the rain pattern of the monsoons in northern Pakistan provides ideal conditions for growing guar gum.
However, also like India, adverse climatic conditions are a key challenge facing Pakistan’s guar gum industry, its production, yields and prices. The negative perception of Pakistani guar gum quality when compared to Indian guar gum is a key challenge facing the industry. Outdated processing facilities which undermine quality is another key challenge facing Pakistan. European buyers sometimes experience quality issues with Pakistani guar gum.
China
Eurostat data shows China was the third-largest exporter of guar gum to the European market in 2020 in terms of volume. China has an established commercial guar gum production industry which is developing, one of the country’s key strengths. China’s good level of infrastructure is likely to make it easier for exporters, however, Chinese suppliers cannot usually compete with India suppliers in volume.
Sudan
Eurostat data from 2020 showed Sudan was the largest exporter of gum arabic to Europe in terms of volume in 2020. One of Sudan’s key strengths is that it has a well-established commercial gum arabic production industry, with gum arabic extensively cultivated. The acacia tree from which gum arabic is produced is native to the Sahel, where Sudan has the densest acacia forests among countries in the region. Sudan also produces high-grade gum arabic at local processing facilities.
However, key challenges facing Sudan’s gum arabic industry include expansion of farming schemes at the expense of forests where gum arabic is cultivated, poor harvesting and post-harvesting techniques, lack of adequate infrastructure, large government taxes and climate change.
Even though there is some processing of gum arabic in Sudan, it is considered a basic level of quality, which hampers the development of the gum arabic industry in the country.
Other challenges facing Sudan include gaps in the business environment and significant corruption. Economic sanctions, internal conflicts, and a lack of a stable political system and infrastructure, give a negative impression of Sudan to European businesses. In the latter part of 2021, Sudan was experiencing political instability as a result of a military coup that took place in October. This can negatively affect trading partnerships with European buyers and Sudanese exporters. European manufacturers have strong business relationships with Sudanese gum arabic exporters. However, large importers and processors of gum arabic in Europe have their own presence in Sudan to control quality and ensure smooth supply.
Chad
Eurostat data showed Chad was the second-largest exporter of gum arabic to Europe in 2020 in terms of volume. One of Chad’s key strengths is that it has an established commercial gum arabic production industry. In recent decades, Chad has made significant progress in terms of the quantities and quality of gum arabic it produces.
Chad’s government supports for the country’s gum arabic industry are expected to double gum arabic export volumes in the next five years. However, European buyers sometimes find gum arabic from Chad unreliable in terms of delivery.
Key challenges facing Chad’s agricultural sector include its significant vulnerability to climate change, environmental degradation and poor infrastructure. Other challenges facing Chad include it being geographically isolated, therefore making it difficult to export, high levels of corruption, and worsening security conditions, as well as low stocks of gum arabic.
Nigeria
In terms of volume, Eurostat data shows Nigeria was the third-largest exporter of gum arabic to Europe in 2020. One of Nigeria’s key strengths is that it has an established commercial gum arabic production industry. Since the 2000s, Nigeria has produced high-grade gum arabic at local processing facilities, yet another of its key strengths.
The Nigerian government has implemented special interventions to develop its gum arabic industry in recent years. For example, establishing the gum arabic production enhancement input support scheme, as well as providing farmers with high-quality seedlings. It may therefore become easier for Nigerian producers of gum arabic to enter the European market. However, key challenges facing the Nigerian gum arabic industry include political instability and insecurity in growing regions, quality, climate change, pests and diseases.
Nigeria’s gum arabic industry has also been hindered by quality inconsistency, poor market organisation and production disruptions due to the Boko Haram insurgency in recent years.
Tips:
- Find out if your country has programmes to help exporters like you to harvest, cultivate, produce and export guar gum and gum arabic. Check websites and contact the ministry of trade or equivalent in your country which are likely to have information and be able to provide assistance for you to export your product.
- Consider joining organisations such as the Association for International Promotion of Gums which offer assistance to gum arabic producers in developing countries.
- Position yourself against competing countries. For example, if you are a gum arabic producer from Cameroon, inform European buyers about the EU-Cameroon Economic Partnership Agreement, which makes it easier to import gum arabic to the European market.
Which companies are you competing with?
Successful companies exporting guar gum or gum arabic to the European market position themselves as being able to deliver high-quality products in accordance with common European buyer requirements, as well as requirements for niche markets. These companies look reputable in the European market because meeting such requirements gives them credibility.
Established companies have a professional website containing well-prepared content, including sections informing prospective buyers about who they are, how they source and process their guar gum or gum arabic along with technical details, as well any certifications they hold and professional photographs.
Indian Companies
Supreme Gums Pvt.Ltd. is an established Indian company exporting guar gum to the European market. One of Supreme Gums’ key strengths is its ability to export high-quality guar gum. Importantly, the company has Food Safety System Certification (FSSC) 22000 and International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 22000:2005 certification, which prove that they have good food management standards for their products. The company also has a strict quality control system with its own in-house laboratory.
Pakistani Companies
Karachi Gum Industry is an experienced Pakistani company exporting guar gum to the European market. The ability to export high-quality guar gum is one of Karachi Gum Industry’s key strengths. Managed by qualified and experienced staff, Karachi Gum Industry has an in-house quality control laboratory. The company is ISO 9001:2008 certified, which shows it has a quality management system for its products.
Sudanese Companies
Afritec’s is a leading Sudanese company exporting gum arabic to the European market. One of its key strengths is its ability to export high-quality gum arabic. The company’s quality department is able to guarantee quality through all stages of the production process, in compliance with international requirements and standards. This is done through its in-house quality control laboratories and compliance with Hazard Analysis Control of Critical Points (HACCP) procedure.
Tips:
- Consider acquiring certification that attests to the high-quality of your guar gum or gum arabic. For example, FSSC 22000, ISO 22000:2005 and ISO 9001:2008.
- Ensure you have an up-to-date professional website with well-prepared content, which clearly informs prospective buyers of your key strengths, such as your ability to guarantee quality of your product through your quality control procedure.
Which products are you competing with?
Tara gum
Tara gum has been identified as a competing product to guar gum and gum arabic. Just like guar gum and gum arabic, tara gum can be used as a gelatine replacer. Tara gum’s other key strengths include its functional properties, such as being soluble in cold water just like guar gum, as well as its ability to work well with other natural food additives for food, such as xanthan gum or carrageenan. Compared to guar gum, tara gum has a better flavour release along with it not having an unpleasant odour and taste.
Tara gum is used by food manufacturers of a range of products. Tara gum is native to Peru, a major country supplier accounting for 90% of global tara gum exports. Tara gum is also endemic to other South American countries, such as Bolivia, but it is also cultivated in Africa, the Middle East and Asia.
Tara gum’s strengths make it a threat to guar gum and gum arabic. However, a key weakness of tara gum concerns its vulnerability to climatic conditions, leading to small harvests and supply shortages, which cause production problems. Tara gum also faces strong competition from synthetically produced gums and thickeners.
Figure 10: Tara Gum

Source: Adobe Stocks/Akvals
Seaweed extracts
Seaweed extracts — carrageenan and agar agar — are competing products to guar gum and gum arabic. Carrageenan and agar agar are used in the European food and drinks industry because they have a number of functional properties, such as a thickener, stabiliser and gelling agent. This is one of their key strengths allowing formulators to use them across a range of products.
Carrageenan and agar agar are also used by the food and drinks industry because they are an alternative to gelatine and animal-derived ingredients. This is particularly important as there is growing demand for vegan products in Europe.
In recent years, carrageenan and agar agar have received negative press attention because of safety concerns, which is a key weakness factor for them. The European seaweed market is predicted to increase to 2024 partly because of their growing use as food additives in food products , which is allowed under EU regulations. Thus, carrageenan and agar agar are a threat to guar gum and gum arabic.
Figure 11: Agar agar
Source: Adobe Stock/Michelle
Modified starches
Modified starches are also identified as competing products to guar gum and gum arabic. Modified starches are plant-based food additives made from starch extracted from grains and vegetables, such as wheat, maize, and potatoes. Modified starches are used to overcome constraints of using food ingredients that are not always compatible with modern food processing.
Twelve modified starches are authorised as food additives in the EU. This multiple choice is one of modified starches’ key strengths, offering formulators options according to the benefits they provide. For example, E1450 can be used as an emulsifier, thickener, binder and emulsifier. However, strict government policies in the area of the modified starch limits this industry. Despite this, the European starch market is expected to increase until 2023. Thus, modified starches are a threat to guar gum and gum arabic.
Tips:
- Familiarise yourself with products competing with guar gum and gum arabic that are available in the European market to learn about their strengths and weaknesses. Read related reports like the CBI study on seaweed extracts for food.
- Position yourself against competing products. Do this by highlighting your company as well as the strengths of guar gum and gum arabic, for example, providing certification to demonstrate the high quality of your product.
- Build a marketing story for your guar gum and gum arabic, placing emphasis on their key strengths. Afritec is a Sudanese company exporting gum arabic doing just this, by clearly informing prospective buyers about its ingredient’s key strengths. For example, its gum arabic goes through a strict quality control process before it reaches European buyers.
What are the prices for gums on the European market?
The price of spray-dried Senegal gum arabic ranges between US$2/kg and 2.5/kg (FOB), while the price of Seyal gum arabic ranges between US$0.5/kg and US$0.10/kg (FOB). The price of Indian guar gum ranges between US$1.0/kg and US$2/kg (FOB), with oil prices being a key influencing factor. The price of guar gum from Pakistan is similar to the price of guar gum from India.
According to European buyers, several factors influence the price of guar gum and gum arabic, including changing harvest patterns, availability, and oil prices, along with quality differences and climate change, which affects weather patterns, such as the monsoon. For example, a delayed monsoon affects harvest patterns because farmers have to delay their sowing pattern for the new season, which raises product prices.
Tips:
- Carefully calculate the price breakdown of your guar gum or gum arabic carefully before setting and agreeing on prices with European buyers, so you can recover your production and export costs, and still make a profit.
- Consider offering discounts to buyers ordering guar gum and gum arabic, particularly with large orders, whose buyers are used to it. To avoid facing losses, ensure you include discounts offered in your original calculations, so that you do not sell at a lower price than your costs.
- Consider obtaining certifications to make your guar gum or gum arabic more competitive in the European market. Having relevant certifications will also help you justify a higher price.
This study was carried out on behalf of CBI by Ecovia Intelligence.
Please review our market information disclaimer.
Search
Enter search terms to find market research