
What requirements must processed fruit, vegetables and edible nuts comply with to be allowed on the European markets?
Exporting processed fruit, vegetables and nuts to Europe means you need to meet high standards for food safety and quality. Food consumed in the European Union (EU) is largely free of harmful residues. However, limits on various contaminants keep rising. Increased traceability, transparency and responsible social and environmental practices are becoming more important. This has led to the development of lots of certification schemes. There are also opportunities to stand out from the market by applying niche market standards.
Contents of this page
- What are the mandatory requirements for processed fruit and vegetables and edible nuts?
- What additional requirements and certifications do buyers ask for in the processed fruit and vegetable and edible nuts sector?
- What are the requirements and requested certifications in the niche processed fruit, vegetable and edible nuts markets?
1. What are the mandatory requirements for processed fruit and vegetables and edible nuts?
The General Food Law is the legislative framework for food safety in Europe. The General Food Law established the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EFSA is responsible for developing specific food safety legislation and creating frameworks for official food controls.
This law is based on the “Farm to Fork” approach. This means that all food has to be traceable throughout the entire supply chain. Over 100,000 people in Europe are part of the official controls of 25 million operators in the food supply chain. This chain also includes non-European suppliers. To ensure food safety for European consumers, every food operator needs to implement the Hazard Analysis of Critical Control Points (HACCP) system into their daily operations.
If companies do not comply with European food legislation, individual cases can be reported through the Rapid Alert System for Food and Feeds (RASFF), which is freely accessible to the general public.
Figure 1: Farm to Fork approach

Source: European Commission
Be aware of tariff barriers
Tariffs are duties that the importer normally pays. The amount of the tariffs depends on the trade agreements between Europe and the supplying country. For most processed fruit, vegetables and nuts imported from developing countries, there are either low tariffs or none at all. To benefit from these low tariffs, most fruit and vegetables must be sourced in the supplier country before processing. There are a few examples where this does not apply, such as in jams where sugar can be imported.
Tariffs for processed fruit and vegetables are calculated in one of three different ways:
- Ad valorem tariffs: a percentage of the import value. For example, single-strength orange juice imported from Brazil has an ad valorem tariff of 12.2%;
- Specific tariffs: a value added to imported quantities. For example, a tariff of €4.20/100 kg is applied on cocktail cherry imports from Türkiye;
- Combined tariffs: a combination of ad valorem and specific tariffs. For example, an ad valorem rate of 24% and an extra rate of €23/100 kg is applied to imported strawberry jams from China.
Tariff quotas are another kind of tariff barrier. One example is the import of olive oil from Tunisia, where zero tariffs are applied. Once 56,700 tonnes have been imported, a regular tariff of €124.50 per 100 kg applies.
Tips:
- VVisit the EU Access2Markets portal to find for more information on tariffs, import rules and taxes that apply to products exported from your country.
- Use the Market Access Map to analyse potential competitive advantages based on applied tariffs for your country and others.
- Contact Open Trade Gate Sweden if you have questions about rules and requirements in Sweden and the European Union.
- Register on the EPing platform to receive email alerts about upcoming changes to product requirements.
Get a phytosanitary certificate for in-shell nuts
Phytosanitary certificates are currently needed for plants and plant products that can be grown in Europe after import, including in-shell nuts. However, be aware that a new draft regulation is being discussed, which might extend controls to include all nuts and dried fruits.
Check if increased border control is requested for products from your country
If a country does not comply with European food legislation multiple times, this may lead to stricter import conditions or even suspension of imports from that country. These conditions usually require a health certificate and an analytical test report for a certain percentage of the shipments from specified countries. Products from countries that have shown repeated non-compliance are put on the official laboratory test list provided in the regulations on the increased level of official checks on imports.
Table 1 presents the frequency of controls for processed fruit, vegetables and edible nuts according to the latest issue of the EU border control regulation. An additional temporary regulation for increased control was published in May 2022.
Table 1: Official controls for processed fruit and vegetables and edible nuts as of July 2024
| Country of origin | Product | Hazard | Frequency of official controls (%) |
| Argentina | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 5 |
| Azerbaijan | Hazelnuts, hazelnut oil, hazelnut powder and hazelnut paste | Aflatoxins | 20 |
| Bolivia | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Brazil | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 10 |
| Brazil | Brazil nuts in shell | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Cambodia | Frozen yardlong beans | Pesticide residues | 50 |
| Côte d’Ivoire | Palm oil | Sudan dyes | 20 |
| China | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 10 |
| Dominican Republic | Frozen chillies and paprika | Pesticide residues | 50 |
| Dominican Republic | Frozen yardlong beans | Pesticide residues | 30 |
| Egypt | Frozen chillies and paprika | Pesticide residues | 30 |
| Egypt | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 20 |
| Georgia | Hazelnuts, hazelnut oil, hazelnut powder and hazelnut paste | Aflatoxins | 30 |
| Gambia | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Ghana | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Ghana | Palm oil | Sudan dyes | 50 |
| India | Frozen moringa | Pesticide residues | 30 |
| India | Frozen okra | Pesticide residues | 20 |
| India | Frozen yardlong beans | Pesticide residues | 30 |
| India | Frozen curry leaves | Pesticide residues | 50 |
| India | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| India | Frozen chillies | Pesticide residues | 30 |
| India | Sauces and seasonings | Pesticide residues | 20 |
| Iran | Pistachios, pistachio paste and pistachio powder | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Kenya | Frozen chillies | Pesticide residues | 10 |
| Lebanon | Pickled and preserved turnips | Rhodamine B | 50 |
| Madagascar | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Mexico | Tomato ketchup and other tomato sauces | Pesticide residues | 10 |
| Nigeria | Watermelon seeds | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Pakistan | Frozen chillies | Pesticide residues | 20 |
| Rwanda | Frozen chillies | Pesticide residues | 20 |
| Sri Lanka | Frozen yardlong beans | Pesticide residues | 20 |
| Sri Lanka | Frozen chillies and paprika | Pesticide residues | 50 |
| Senegal | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Sierra Leone | Watermelon seeds | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Sudan | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Syria | Tahini and halva from Sesamum seeds | Salmonella | 20 |
| Syria | Pickled and preserved turnips | Rhodamine B | 50 |
| Thailand | Frozen chillies | Pesticide residues | 30 |
| Türkiye | Frozen chillies and paprika | Pesticide residues | 20 |
| Türkiye | Dried figs, dried fig paste and dried figs flour | Aflatoxins | 20 |
| Türkiye | Pistachios, pistachio paste and pistachio powder | Aflatoxins | 50 |
| Uganda | Frozen chillies | Pesticide residues | 50 |
| United States | Groundnuts, groundnut flour, groundnut paste, peanut butter | Aflatoxins | 20 |
| United States | Pistachios, pistachio paste and pistachio powder | Aflatoxins | 30 |
| Uzbekistan | Dried apricots | Sulphites | 50 |
| Vietnam | Frozen okra | Pesticide residues | 50 |
Source: Autentika Global compilation based on regulations (EU) 2019/1793 from 02.07.2023 and (EU) 2022/913 from 30 May 2022.
Tips:
- Stay up to date with the Official Controls Regulation on the EC website. The list is updated regularly. Even if your country is not on the list, be aware of the most common contaminations for your product. Use all possible preventive measures.
- Search for examples of withdrawals from the market and the reasons for them in the RASFF database.
- Subscribe to the EFSA newsletter (free of charge) to receive news about European food safety developments.
- Implement an HACCP system into your daily practice. Even if HACCP systems are not obligatory in your country, you must meet the European food safety regulations.
Regularly perform a test on the presence of contaminants
Food contaminants are unwanted and harmful substances in food that can cause consumer illness. There may be substances in food because of its production, packaging, transport or storage. They may also come from the external environment.
European inspections have taken strict and extensive measures to minimise contaminants in food. EC Regulations set maximum levels for certain contaminants in food products. This regulation is frequently updated and includes limits for specific products.
Ensure that your product is free of any foreign bodies
Insects are an important contamination issue for dried fruit and nuts in shells imported to Europe. Dead insects can be found in packaging. Some insect types can also develop inside fruit and continue to grow in storage. To prevent insect contamination, suppliers from developing countries should use preventive measures, like fumigation and temperature treatments. Other types of contamination with foreign bodies include dirt, stones, glass and metal parts (for example from agricultural machinery and tools).
Tips:
- UStay up to date with the regularly updated list of the Official Controls Regulation on the EC website. Even if your country is not on the list, be aware of the most common contaminations for your product. Use all possible preventive measures.
- Search for examples of withdrawals from the market and the reasons for them in the RASFF database.
- Implement an HACCP system into your daily practice.
Regularly perform a test on the presence of contaminants
European inspections have taken strict and extensive measures to minimise contaminants in food. EC Regulations set maximum levels for certain contaminants in food products. This regulation is frequently updated and includes limits for specific products.
Ensure that your product is free of any foreign bodies
Insects are an important contamination issue for dried fruit and nuts in shells imported to Europe. To prevent insect contamination, suppliers from developing countries should use preventive measures, like fumigation and temperature treatments. Other types of contamination with foreign bodies include dirt, stones, glass and metal parts (for example from agricultural machinery and tools).
Tips:
- Use metal detectors to prevent contamination from metal particles. Aside from consumer protection, metal detectors will also help prevent damage to your processing machinery. Physical sorting and eye-hand control is always recommended, even with installed detectors.
- Only apply officially approved fumigants like CO2, Phosphine and Sulfuryl fluoride. Methyl bromide and ethylene oxide are banned in the EU.
Minimise microbiological contamination through strict hygiene and sanitary practices
Border rejections of imported processed fruit and vegetables are often related to microbiological contamination. The most common types of microbiological contaminants in processed fruit and vegetables are Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Listeria, Norovirus and Hepatitis A. The European regulation on microbiological criteria for foodstuff sets limits for pathogenic micro-organisms, their toxins and metabolites.
In the fruit and vegetable processing sector, microbiological contamination can be caused by dirty water being used for irrigation, cleaning or processing. Dirty hands, infected handlers, packaging and transport vehicles can also transmit bacteria and viruses. As such, it is important for suppliers from developing countries to teach their employees to use good hygienic practices. More European buyers request pasteurisation to prevent microbiological contamination.
Tips:
- Keep up with the most recent trends on food safety testing developments. More rapid test kits that can be used in daily operations are becoming available.
- Follow the Codes of Hygienic Practice published by Codex Alimentarius to prevent microbiological contamination.
- Check how to minimise the risk of microbial contamination of berries (PDF) on the European Association of Fruit and Vegetables Processors webpage.
- Read the guidelines for produce washing (PDF) and check the water for cleaning and processing fruit and vegetables regularly.
Prevent mycotoxins with good post-harvest processing and storage practices
Mycotoxins are toxic substances produced by fungi, more commonly known as moulds. These toxins are very stable and can survive intensive processes like heat treatment. The most common mycotoxin contaminations in the processed fruit and vegetables sector are aflatoxins, ochratoxin A and patulin.
- Aflatoxins are the most common mycotoxins found in edible nuts, especially in groundnuts. They are also found in dried fruit. The maximum level of aflatoxins for most nuts and dried fruit intended for direct human consumption must be below 2 μg/kg for aflatoxin B1. Total aflatoxin content must be below 4 μg/kg;
- Ochratoxin A is a mycotoxin that is most commonly found in dried fruits, especially grapes, but it is also found in grape juice. Ochratoxin A is difficult to prevent because its growth is linked to climatic conditions. The limit is 8 μg/kg for dried grapes and figs, 2 μg/kg for other dried fruit and grape juice, 5 μg/kg for pistachios and 0.5% for baby food;
- Patulin is associated with mouldy fruits and vegetables. In particular rotting apples and figs. Different types of fruit juice have limits between 10 and 50 μg/kg;
- Alternaria toxins are currently being investigated by the EFSA. Although there are no limits, there are recommendations for indicative levels for products like processed tomatoes, tree nuts and dried figs.
Control of mycotoxins is best achieved by pest management in orchards and good post-harvesting practices, such as timely harvesting and proper drying after harvests. Appropriate moisture and temperature conditions during storage and transport, and the timely detection and removal of contaminated material from the supply chain are also important control measures. Automatic colour sorting and hand sorting is often used to remove mouldy nuts.
Tips:
- LFollow the Codex Alimentarius codes of practice for tips on the prevention and reduction of aflatoxin contaminations in tree nuts, peanuts and dried figs. Also refer to the FAO guidance for prevention of aflatoxin in pistachios.
- Check the Transport Information Service website for information on safe storage and transport of processed fruit and vegetables and edible nuts.
Limit the use of pesticides
The EU maintains a list of approved pesticides that are authorised for use. This list is often updated and there is a general trend to lower pesticide limits. The European Directive on Maximum Residue Levels of Pesticides defines these MRLs, so you should check it frequently.
One of the aims of the Farm to Fork strategy is to reduce the use of chemical pesticides by 50% by 2030. New measures will guarantee the use of integrated pest management. This is an environmentally friendly pest control system. It focuses on preventing pests and prioritises alternative pest control methods, so chemical pesticides are only used as a last resort.
Tips:
- UUse the European Union pesticides database to find the relevant MRLs for your products. Select your product or the pesticide you use, and the database will show the list of the MRLs associated with them.
- Use Integrated Pest Management (IPM) to reduce pesticide amounts. IPM is an agricultural pest control strategy that uses natural control practices and forecasting information to minimise spraying with synthetic chemicals. For more information about Integrated Pest Management, see the FAO website.
- Work closely with farmers to have full control of the use of pesticides in your raw materials. Engage with plant protection experts who can regularly guide and advise farmers on the sustainable use of pesticides. For example, by subscribing to a professional weather service, or by using agricultural weather stations, it is possible to forecast the appearance of potential pests and plant illnesses. You can also limit the use of pesticides.
- Check with your buyers if they have additional requirements on MRLs and pesticide use. Many European retailers have stricter MRLs than is legally required.
Control and prevent other contaminants
There are several other contaminants that are commonly controlled via physical and laboratory tests. These include:
- Chlorates and perchlorates – Chlorates are no longer approved as a pesticide, but they can come into contact with food if chemicals are used for water disinfection. Detergents used for cleaning facilities and processing equipment are another potential source. The level of chlorates is 0.05 mg/kg for most fruit and vegetables (including frozen ones), 0.3 for dates and figs, 0.7 for table olives and 0.1 for edible nuts.
- Heavy metals and metalloids – Heavy metals can occur as residues in food because of their presence in the environment or as a result of contamination from farming, processing or pollution. The EU regulation on food contaminants sets restrictions for lead (fruit, fruit juices, oils, various kinds of vegetables), cadmium (tree nuts, fruit and vegetables), mercury (food supplements), arsenic (juices) and tin (canned food and beverages).
- Irradiation – The use of irradiation to prevent microbiological contamination is limited in Europe. European radiation protection legislation and radioactive contamination legislation define the maximum permitted levels of radioactive contamination in food. Fruit and mushrooms picked in the wild may absorb radiation if they are collected in areas of previous nuclear accidents;
- Glycidyl esters – Glycerol-based products are contaminants found in vegetable oils. Roasted nuts and dried fruit should also be checked if they are oiled.
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) – A specific problem related to the production of banana chips is the occurrence of benzo(a)pyrene and PAH. These toxic organic compounds can be formed if banana slices are fried in coconut oil.
- Acrylamide – Acrylamide is a contaminant that may be formed in foods at temperatures of 120°C or higher. The European Commission published its recommendation on the monitoring of the presence of acrylamide in certain foods, including roasted nuts, dried fruits and table olives.
- Specific plant toxins – The presence of tropane alkaloids is controlled for apricot kernels placed on the market for the final consumer. Raw apricot kernels contain amygdalin, which occurs naturally. This results in cyanide being released if the kernels enter the human gut. Raw, unprocessed apricot kernels should not be sold for human consumption unless cyanide levels are compliant with the ML of 20 mg/kg;
- Nitrates – Nitrate levels are checked in frozen spinach.
- Mineral oil hydrocarbons (MOSH/MOAH) – Mineral oils can be found in lubricants for machinery, surface treatment agents and packaging materials. A draft German Mineral Oil Regulation suggests a limit of MOAH of 0.5 mg/kg, which can migrate from packaging to food. Currently, fried and sweetened banana chips seem to be a problem. At the end of 2023, the EU Commission presented a first Draft Regulation to establish maximum levels for mineral oil aromatic hydrocarbons (MOAH).
Tips:
- Check ingredients and instructions for sanitisers to avoid contamination with chlorates and perchlorates. Perchlorates are common in shoe sanitisers. Chlorates are used in water sanitation.
- Check the sampling and analysis guidelines for control of different contaminants.
- Follow the Codex Alimentarius Code of Practice for the Reduction of Glycidyl Esters (PDF) in food made with refined oils.
- Follow the Codex Alimentarius Code of Practice for the Reduction of Contamination of Food with Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PDF) for Smoking and Direct Drying Processes in food made with refined oils.
Be fully transparent about your ingredients and product composition
European authorities can reject products if they have undeclared, unauthorised or excessive levels of food improvement ingredients. There is legislation for additives (for example preservatives, colours, thickeners), flavourings and enzymes that lists the allowed E numbers and substances. Additives that are allowed are listed in Annex II of the Food Additives Regulation. Note that pectin derived from apples, citrus fruits and quince (used in the production of jams and marmalades) is not considered a food additive.
If you want to add vitamins to your product, you have to know what vitamins, minerals, sources and formulations are allowed. Vitamins and minerals can be added to fruit juices and fruit nectars. Maximum levels have not been set yet, but the EC is working on a proposal.
Product-specific legislation about composition applies to fruit juices and fruit jams, jellies, marmalade and sweetened chestnut purée. The directives indicate which raw materials and additives can be used. In the processed fruit and vegetables sector, problems commonly occur due to the undeclared or excessive use of preservatives.
The fruit juice and jams legislation was changed in May 2024. Labelling now needs to better inform consumers about fruit juice content. This helps to address the growing demand for products with lower sugar content. New legislation allows consumers to be made aware that the juice does not contain any added sugars and to indicate “reduced-sugar fruit juice” on its label. The legislation also increases the minimum fruit content of jams from 350 to 450 g per kilogram of finished product (550 g for extra quality).
Product authenticity
Intentionally placing incorrectly declared products on the European market is considered a crime. The main reason for misleading consumers is profit. But many food criminals are unaware that placing undeclared ingredients can present a serious risk to human health. Some substances can cause allergic reactions, and some are toxic. Many laboratories in Europe have increased testing to discover this type of fraud in food.
Some examples of authenticity problems with processed fruit and vegetables include the following:
- Undeclared preservatives, for example sulphites in dried fruit and coconut products or benzoic acid in pickled products;
- Undeclared use of food colouring, for example using Sunset Yellow colouring in dried candied fruit or fruit purées;
- Declaring a false variety of products, for example substituting ‘alphonso mango’ purée with cheaper varieties (e.g. “totapuri”);
- Wrongly declared ratios in fruit mixes, for example increasing the ratio of cheaper berries (e.g. strawberries) and decreasing the share of expensive berries (e.g. raspberries or blueberries).
- Adding water to frozen products – although water glazing is commonly used for some frozen products (e.g. fish), it must not be used in frozen fruit and vegetables;
- Adding water to concentrated juices or purées. Even if adding water fails to decrease the declared Brix level, it is still considered fraud;
- Lower levels of certain types of fruit than declared in retail products. For example, declaring a product as blueberry nectar if the content of blueberry/bilberry juice is lower than 40% is not allowed;
- Wrong quality declaration, such as selling virgin or lampante olive oil as extra virgin.
Tips:
- Stick to the rules! New laboratory testing methods can easily discover non-permitted product additions (e.g. sugars, water and other fruit). It takes a long time and a lot of money to build a good reputation in Europe. Money can be lost very quickly if you are caught tampering with your products or delivering sub-standard products.
- Use the European Commission’s Food Additives Database to check what food additives are allowed in Europe.
- Prepare for potential changes in food additive limits in advance by checking the re-evaluation of food additives on the European Commission website.
- Read the monthly Knowledge Centre for Food Fraud and Quality reports to stay up to date and avoid adulteration issues.
- Regularly implement staff training and awareness programmes to avoid human error related to product composition.
Use safe packaging and informative labelling
Export packaging must be in line with European legislation on weighting. It must also be safe for consumer health and the environment. Packaging made from wood or vegetable materials may need phytosanitary checks. The labelling of packed products must contain information that is important to the consumer.
Be sure that the packaging is well measured
The content of the packaging must correspond with the quantity (in weight or volume) indicated on the label. Importers will check packaging size and weight to ensure that pre-packed products are within tolerable limits.
Use safe food contact materials
Specific health controls apply for consumer packaging materials that come in contact with food (like cans, jars, or bottles). Food contact materials must not transfer their constituents or influence taste and food odour. A new legislation on revision of the rules on food contact materials is ongoing. Substances to be aware of are Bisphenol A (BPA), phthalates and MOSH/MOAH. EFSA is currently performing a hazard assessment for these substances.
Try to use reusable or recyclable packaging
In April 2024, the European Parliament adopted the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation. This regulation should contribute to the transition to a circular economy. The main aim of the directive is to make all packaging in the EU be reusable or recyclable in an economically viable way by 2030. This has consequences for suppliers from non-European countries. For example, single-use plastic will be banned from 2030, and at least 40% of transport packaging, such as pallets, must be reusable (70% from 2040).
Follow labelling rules for bulk and retail packed products
Packed products must ensure sufficient information for customs clearance and final consumers. Labelling requirements for bulk packed and retail packed products are slightly different:
- Labelling of bulk packed products is regulated by the new EU marketing legislation. Labelling must ensure efficient customs clearance and include handling and storage instructions. The export-packaging label usually indicates the name of the product, a better description (e.g. class, grade or style), the packer’s name and physical address, the country of origin, the lot number and an allergen warning. For some products, the harvesting year and cultivar is also indicated;
- Labelling of retail packed products is regulated by the regulation on the provision of food information to consumers. Labelling rules help consumers to make informed choices. This information defines obligations like nutritional information, the presentation of allergens, indication of origin and mandatory font size. The European nutrition and health claims legislation forbids claims that any food can prevent, treat or cure a human disease;
- Labelling of origin and the marketing standard is regulated by the marketing regulation, which entered into force in November 2023. According to this regulation, the country of origin and the ingredients in mixes must be labelled. Marketing standards will also be applied to processed fruit and vegetables and edible nuts. It is expected that the labelling of juices, purées and jams will indicate the origin of fresh fruit and vegetables used for processing before 2027.
To better inform consumers about healthier food choices, several voluntary nutritional labelling schemes were developed in Europe. The most famous is Nutri-Score, but there are other schemes such as Nutriform battery (Italy), Front of Pack Nutritional Labelling (also known as ‘traffic light’, the UK) or Keyhole (Sweden).
Figure 2: Examples of front-of-pack nutritional labelling used in Europe
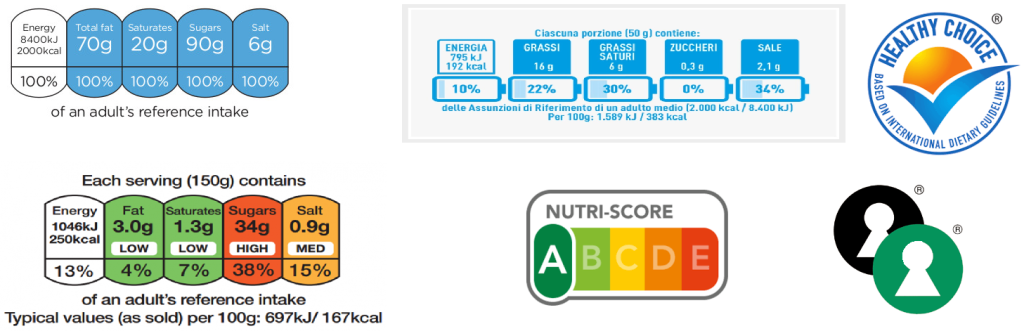
Source: Autentika Global
Tips:
- Visit the Access2Markets website for more information on food labelling.
- The presence of allergens is becoming increasingly important. The chance of cross-contamination (for example, if a product is processed in a factory that also processes peanuts) can even happen at farm level.
- For product-specific packaging requirements, read product-related studies about promising export products.
- Be aware of the new plastic packaging rules in Europe and make sure to adapt to new packaging materials in time.
- Perform a basic analysis for nutrition at least annually if you aim to place a retail packed product on the European market.
Novel foods must be authorised before entering the European market
‘Novel food’ refers to all foods that were not consumed much in the EU before May 1997. Novel food can be newly developed. It is innovative food, produced using new technologies and production processes, as well as food that is or has been traditionally eaten outside the EU. Novel food must be approved, safe for consumption and properly labelled. Examples of novel foods are baobab juice, maca powder, galip nuts and food produced using the latest technological innovations (such as high-pressure fruit juice).
The regulation on novel foods defines conditions for food businesses bringing new and innovative foods to the European market. This regulation requires the evidence of safe use in at least one country outside of the EU for a period of 25 years. A notification is sent to the EC and then forwarded to all member states and EFSA. A member state or the EFSA may submit safety objections to the traditional food in question within four months of receiving a valid notification.
Tips:
- Check the Novel Food status Catalogue to see if your product or ingredient is authorised as a novel food. Note that the list is non-exhaustive. It serves as an orientation on whether a product will need authorisation under the Novel Food Regulation. Also check the Union list of novel foods. It shows novel foods that do not need notification.
- If you want to submit a new product as a novel food, use an online application for authorisation.
Comply with the legislative requirements on sustainability
Some of the most relevant European laws and legislation related to environmental and social sustainability have been incorporated in the European Green Deal (EGD). The EGD is a set of policies whose aim is to lead Europe to climate neutrality by 2050. Climate neutrality means reaching the balance between GHG emissions and removals which is expected to limit global warming. This state is known as zero emissions and can be reached if global warming is limited to 1.5°C.
Figure 3: Farm to Fork Strategy aspects
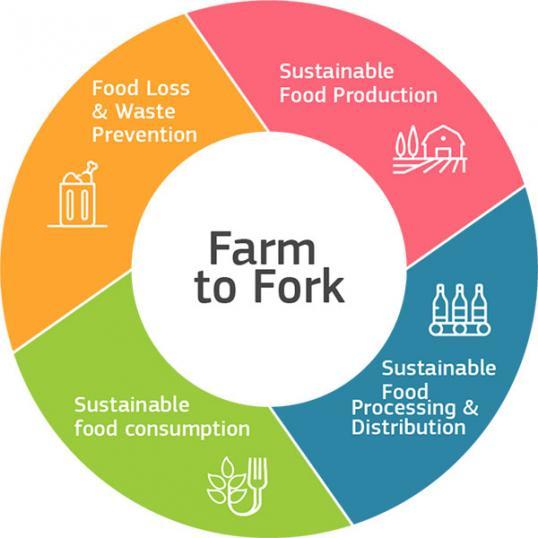
Source: European Commission
The EGD includes legislative changes and a timetable outlining when they will come into action. The most relevant policies for the fruits, vegetables and nuts processing sector are the Farm to Fork Strategy, the Biodiversity Strategy and the Circular Economy plan. The polices included in the Farm to Fork Strategy are presented in Figure 3 above. Specific legislations related to those strategies relevant for fruits, vegetables and nuts processing and trade are related to:
- Organic food regulation (in force);
- Sustainability labelling of food products (proposal);
- Deforestation free products (in force);
- The Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (in force since July 2024);
- Packaging and packaging waste (in force);
- Sustainable use of pesticides (in force but under review).
Tip:
- To prepare for the legislative changes in line with the EGD and Farm to Fork Strategy, read CBI’s Tips to go green and Tips for becoming a socially responsible supplier.
2. What additional requirements and certifications do buyers ask for in the processed fruit and vegetable and edible nuts sector?
European buyers also need additional food safety certification awarded by independent control bodies. Some buyers have their own lists and quality requests. In addition, more buyers are demanding proof of sustainable and ethical business practices.
Describe the quality of your product in line with the industry standards
The quality of processed fruit and vegetables is determined by various factors, depending on the product type. For example, for frozen and dried fruit and vegetables and for edible nuts, quality categories are mainly defined by the allowed percentage of defective produce and fruit size. For homogenous products such as juices, purées or fruit spreads, there are many quality criteria. These include colour, flavour, chemical composition and Brix level (sugar content in water solution).
Quality criteria are defined by industry standards and official European legislation. The most common quality standards for specific products include the following:
- Frozen fruit and vegetables quality – mostly defined by Codex Alimentarius standards. Currently, Codex standards apply to many frozen products, including peas, several types of berries, peaches, broccoli, cauliflower, spinach, Brussels sprouts and green beans. The industry has set many additional criteria to determine the quality of frozen products. For example, the Brix level and flavour of frozen fruits is important for the processing industry, while retailers value a uniform shape, size and colour.
- Dried fruit and nuts quality – commonly defined by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) standards. UNECE standards apply to many nuts, including almonds, Brazil nuts, cashews, coconuts, hazelnuts, macadamias, pine nuts, pistachios and walnuts. UNECE standards for dried products include apricots, bananas, grapes, mangoes, melons, papayas, pears, pineapples, prunes and tomatoes. New European marketing legislation also includes quality standards for this subsector.
- Fruit and vegetable juice quality: in Europe this is based on the EU Fruit Juice Directive and on the Industry Codes set by the European Fruit Juice Association. The European Fruit Juice Directive defines several quality aspects, such as authorised ingredients, labelling rules and minimum Brix levels for reconstituted fruit juices and purées. There is also a Codex Alimentarius standard for fruit juices and nectars.
- Jams, jellies and marmalades quality: in Europe, this is based on the European regulation for fruit jams, jellies and marmalades and sweetened chestnut purée. This regulation defines a minimum content of fruit pulp and/or purée in finished products. There are many other product characteristics not included in European legislation that define quality, such as consistency, fruit Brix level, colour, taste and type of sweetener used. There are also Codex Alimentarius standards for jams (PDF).
- Canned fruit and vegetables quality: usually defined by several Codex Alimentarius standards and Guideline Procedures for the Visual Inspection of Lots of Canned Foods. Codex has published standards for processed tomatoes, apple sauce, canned pineapples, canned raspberries, canned strawberries, fruit cocktails, tropical fruit salad, chestnuts and chestnut purée, mango chutney, canned bamboo shoots, canned stone fruits, pickled fruit and vegetables, certain canned vegetables, coconut milk and cream.
Get Food Safety Certification
Although food safety certification is not obligatory under European legislation, it has become a must for almost all European food importers. Most established European importers will not work with you if some proof of food safety certification is not provided. Most European buyers request a Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) recognised certification. For fruit, nuts and vegetable processors and traders, the most popular certification programmes are:
- International Featured Standards (IFS);
- British Retail Consortium Global Standards (BRCGS);
- Food Safety System Certification (FSSC 22000).
Although different food safety certification systems are based on similar principles, some buyers may prefer one specific management system. For example, British buyers often require BRC, while IFS is more common for German retailers. Also note that food safety certification is only a foundation to start exporting to Europe. Serious buyers will usually visit or audit your production facilities before signing a contract.
In the fruit juice industry, the most important development is the voluntary control system developed by SGF. For bulk juice processors, a part of this certification system is called IRMA (International Raw Material Assurance). Apart from fruit processors, a specific IRMA certification is also applicable to traders/brokers, transport companies, storage facilities and tank cleaning. There is also a specific certification for bottling companies: IQCS (International Quality Control System for juices and nectars).
Traceability is a key requirement in each of the certification schemes listed above. In practice, this means that you should be able to trace back each lot of packed and processed products to the fresh fruit, vegetables and in-shell nut suppliers.
Be ready for additional food safety checks
In practice, food safety certification, although almost mandatory, is less important than the physical approval of the products. Buyers in Europe regularly perform laboratory tests. It is common practice in Europe for deliveries to be accompanied with documentation from accredited laboratories, no more than six months old.
The credibility of laboratories that perform testing is important for European buyers. This can be a potential issue for some developing country exporters, as laboratories must be able to deal with all required tests. In some developing countries, laboratories can perform only a limited number of tests. For some analyses, samples have to be sent to other countries. It is common that European buyers ask for tests for more than 500 different pesticide residues.
An emerging issue, especially in nut-processing, is the request for use of pasteurisation/sterilisation equipment. This is a challenging request for many suppliers, as this equipment is expensive. Very strict buyers may also ask for an independent germ kill efficacy test (also called ‘kill step validation’).
Some buyers may insist on following strictly prescribed plant protection plans and only using pesticides from specifically developed lists. By following these plans and using integrated pest management, you can achieve residue-free products. This means that any active ingredient is measured at under 0.01 ppm when analysed under European regulations for maximum residue levels.
Tips:
- Get food safety certification. However, check with the importers and experts if the food safety certification company you consult is acceptable for EU buyers. Examples of independent internationally accredited certification companies include SGS, CIS, TÜV and Bureau Veritas.
- To be more competitive in the European market, try to offer your buyers traceability back to the farmer;
- Consider becoming a member of SGF if you supply raw materials for the European juice industry.
- Be sure to use only ISO/IEC 17025 accredited laboratories when performing microbiological tests.
Comply with the specific requirements of European retail chains
Most European retailers support the certification schemes listed above, but many have additional requirements. A lot of supermarket chains will require suppliers to meet quality assurance standards. This may involve unannounced inspections at processing your facilities.
Most leading European retail chains require every part of the supply chain to be food safety certified. This includes processors in developing countries, shipping companies, packers in Europe, brokers and agents. Until recently, many retailers accepted basic HACCP certification, but GFSI certification is now required for every part of the supply chain.
Another common requirement of the retail chain is the reduction of MRL limits. For example, Lidl’s MRLs limits are 33% lower than official regulations, 70% lower in REWE and Edeka in Germany and 80% lower in ALDI in the Netherlands and Germany. Some retailers have even banned certain pesticides (for example Marks & Spencer).
Sometimes, suppliers of dried fruit, frozen fruit and vegetables and nuts must be additionally audited or certified if they aim to supply specific retail chains. Several European chains have developed special certification modules in addition to GlobalGap. Examples of these audit schemes are Tesco Nurture (by Tesco), Pesticide Transparency Add-on (by Coop Italia) and AH-DLL GROW Add-on (by Albert Heijn and Delhaize).
Apply additional social and environmental sustainability standards
Social, environmental and ethical activities in the European processed fruit and vegetables industry are very important. These activities are implemented and monitored from the farm and production level to the processing (factory) level and up to delivery to the final consumer. Companies have different sustainability requirements. Some companies will require suppliers to adhere to their code of conduct or follow international standards.
The most common international standards used in the sector include:
- Independent audits focused mostly on labour conditions – such as SMETA (by Sedex), amfori BSCI, Ethical Trading Initiative (ETI) and B Corp.
- Labelling and certification schemes focused on environmental impact – such as Eco Score, Eco Impact, Planet Score and Enviro Score. There are currently more than 200 schemes used in Europe. Many of them focus on carbon emissions in the supply chain. In order to prevent greenwashing and to harmonise voluntary green claims, the European Commission published a proposal for a Directive on Green Claims.
- Certification schemes focused on ethical treatment and fair payment of farmers and hired labour – such as Fairtrade (by FLOCERT) and Fair for Life.
- Certification schemes combining social and environmental aspects – such as UTZ, which is now part of the Rainforest Alliance.
To improve the sustainable production and sourcing of nuts, a group of companies and organisations, mainly from Europe, formed the Sustainable Nuts Initiative. Its main objective is to improve conditions in nut-producing countries and help create sustainable supply chains. Fruit juice industry leaders formed the Sustainable Juice Covenant (SJC) with the global aim of making sourcing, production and trade of fruit and vegetable-derived juices, purées and their concentrates 100% sustainable by 2030.
Table 2 below provides a summary of the most important certification and audit schemes in the processed fruit, vegetables and edible nuts sector. Please note that costs for companies are difficult to estimate and cannot be generalised. Only a rough estimation is provided, as final cost depends on a wide range of factors, like the location of the auditor. If the auditor has to travel from another country to your facility, travel expenses and daily fees can significantly increase costs.
Table 2: Most important certifications requested by buyers in the processed fruit and vegetables sector
| Name of certification | Type | Cost for companies | Most used in European end market(s) | Further information on getting certification |
| International Featured Standards (IFS) | Food Safety | The cost of certification is not fixed. It depends on the number of products, the number of certification days and company size. The average price for the 2-day audit for SMSs and 3-5 products is usually around €3,000. Additional costs include annual re-certification. Initial certification may include infrastructural investments (separate cost). | Germany France Recognised in many other European markets | IFS training courses can be purchased from the IFS shop. More details on costs can be found by contacting IFS certification bodies and auditors. Contact consultants to prepare for the certification. Use the IFS Audit Time Calculator to calculate audit duration. Use the smart phone application IFS Audit Manager to perform a self-assessment. |
| British Retail Consortium Global Standards (BRCGS) | Food Safety | There is no fixed fee. It depends on the company size, the number of products and your role in the supply chain. BRCGS certification costs are usually higher than FSSC 22000 certification costs. Typical certification costs for a small company with up to 3 products are around €3,500. For many companies, it is common to be certified with one more scheme in addition to BRCGS. If you take this approach, certification cost may be lower if both certificates are issued by the same body. Additional costs include accommodation costs for the auditors and an annual fee for A and B ranks. For C ranks, audits are performed every 6 months. | The UK retail market mostly recognised in other markets too. | To find a consultant training provider, or certification body, visit the partner sections of the BRCGS website.
|
| Food Safety System Certification (FSSC 22000) | Food Safety | The certification fee depends on the company size, the number of audit days and the number of products. For small companies (<20 employees), the number of products influences the cost, but it is typically in the range of €1,500 – €3,500. An additional fee is paid for annual audits. The audit certificate is valid for 3 years. Typically, additional costs include a consultancy fee for the preparation of the first audit and may also include infrastructural investments. | The Netherlands Italy France Spain Switzerland Scandinavia | Find FSSC 22000 certification preparation courses in your country to prepare for the certification. Find a list of conformity assessment bodies to ask for an offer. |
| International Raw Material Assurance (IRMA) | Quality, safety and authenticity of the juice raw material industry | IRMA certification is a part of the SGF annual membership fee. The fee is based on the annual turnover and number of production sites. For example, for a turnover of €500,000 and one production site, the fee is €5,000. The minimum fee is €5,000 and the maximum is €50,000. | Most used in Germany but relevant for all European markets. | Check the IRMA audit checklist (PDF) to assess your certification readiness. Calculate the annual fee using the IRMA fee calculator. |
| Sedex Members Ethical Trade Audit (SMETA) | Social audit focused on working conditions | Certification costs include a membership fee and £150 per audit. The costs of the first certification are agreed with the agency and not fixed but for most SMEs it is around €1,000. | The UK Germany Most European buyers recognise the SMETA audit as a valid assessment | Check SMETA Guidance documents (PDF) to become familiar with the certification process. |
Business Social Compliance Initiative (amfori BSCI) | Social audit focused on working conditions | Certification cost is not fixed and is agreed with the audit company. Generally, the fee for SMSs is similar to SMETA audit costs, which are around €1,000. | Germany The Netherlands | Check the list of amfori BSCI auditing, training and consultancy companies to ask for an offer for your company. |
| Fairtrade | Sustainability and ethics | There is no fixed fee. Certification costs for fruit processing companies depend on the number of hired workers, the number of products and the number of processing plants. For example, the fee for an SME that employs 20 people and wants to certify 2 products would be around €3,000 for the first year. This includes the application, certification and the processing fees. | The United Kingdom Germany Benelux | Check Flocert Cost Calculator to make an initial assessment of potential certification costs. |
| Rainforest Alliance | Environmental | There is no fixed fee. A request for the offer must be sent to the authorised certification body. Total costs include administrative costs, audit fees, a premium paid to farmers, sustainability investment costs and a volume-based royalty. | It is used in all European countries but more common in West and North Europe. | Find the authorised certification body in the Rainforest Alliance directory to ask for the certification cost. |
| Organic | Sustainability, environmental | Products must be certified at the farmer level before being processed. The fee for individual farmers is considerably lower if famers are united in an association and pay a joint fee. Average fees are around €1,000 for SMEs and the certificate must be renewed every year. | All European countries have their own national organic labels. | Contact EU authorised control bodies in your country to check certification costs. |
Source: Autentika Global
Tips:
- Consider implementing management systems, such as ISO 14001 (environmental aspects), OHSAS 18001 (occupational health and safety), ISO 26000 (a comprehensive system including all social responsibility aspects) or SA 8000 (labour and working conditions). These systems are good ways to address sustainability and possibly gain a competitive advantage.
- Read more about specific sustainability and other requests in CBI’s Tips to go green, CBI’s Tips on Becoming a socially responsible supplier and CBI’s product-specific studies.
- Consult the Sustainability Map database for different standards.
Negotiate realistic delivery terms with your buyer
It often takes three to five weeks for processed fruit and vegetables to be delivered to European ports. If your buyer expects faster delivery, you can check what is realistic and consider working with other reliable processors in your country. However, if you need to combine processing to cut delivery time, you have to approve this with your buyer, as traceability becomes complicated when products are processed and packed in different facilities.
Tip:
- Read CBI’s Tips for organising your processed fruit and vegetables export to Europe to learn more about delivery terms in this sector.
3. What are the requirements and requested certifications in the niche processed fruit, vegetable and edible nuts markets?
Specific requirements apply to niche markets, such as the organic segment and ethnic dietary markets.
Make a cost-benefit analysis for organic certification
Organic certification schemes are increasingly popular in Europe. Although organic production was reserved for niche markets until relatively recently, they are now becoming mainstream. However, certain types of organic certifications, such as ‘biodynamic’ (Demeter or BDA), can still be considered niche requirements.
Farmers, processing and packaging facilities must be audited by an accredited certifier before exporters can put the EU organic logo on their packaging. This also applies to standard holder logos, like the Soil Association in the United Kingdom, Naturland in Germany and Agriculture Biologique in France. The social aspect is now important in almost all organic standards.
To market processed fruit and vegetables and edible nuts as organic in Europe, they must be grown using organic production methods according to European legislation.
The certification procedure generally follows these 6 steps:
- Step 1 – Follow organic production rules according to the European Organic Legislation;
- Step 2 – Apply for certification – small farmers can save costs by applying for group certification;
- Step 3 – Inspection – after the audit, a control body decides if a certificate can be issued;
- Step 4 – Certification – after approval, you can put the EU organic logo on your products;
- Step 5 – Recertification – an organic certificate is valid for 1 year from the issue date;
- Step 6 – Submitting the certification of inspection – every organic products shipment must be accompanied by an inspection certification from the selected certifier. This is done electronically through the central platform called TRACES.
The new organic regulation is accompanied by more than 20 secondary acts. Some of the important acts to be aware of are:
- Detailed organic production rules;
- The list of authorised substances for plant protection; and
- The rules on documentation requirements for imports.
Tips:
- Consider investing in organic production and making a cost-benefit analysis. Organic production will often make production more expensive. However, you may be able to make up for this through higher prices. Demand for certified organic processed fruit and vegetables is increasing.
- Read the training materials on the new organic regulation (by the Alliance for Product Quality in Africa project) to prepare for the new rules on time.
Explore the demand for Fairtrade and ethical certified products
The two most-used sustainability certification schemes are Fairtrade and the Rainforest Alliance. Fairtrade International has developed a specific set of standards for processed fruit and vegetables and edible nuts for small-scale producer organisations. These standards define protective measures for farmers and workers in processing facilities. The standards also define terms of payment, Fairtrade minimum and premium prices for conventional and organic products from several countries and regions.
Tips:
- Consult the ITC Standards Map database for a full overview of certification schemes.
- Respect human rights throughout the whole supply chain. Avoid making deals with companies that do not treat farmers and employees in a fair and sustainable way.
Ethnic and dietary certification
Islamic dietary laws (Halal) and Jewish dietary laws (Kosher) mean believers have specific restrictions on their diets. If you want to focus on the Jewish or Islamic niche markets, you should consider the implementation of Halal or Kosher certification schemes. Due to the increasing popularity of vegan food, many retail brands now also add the V-label logo as proof that the product does not contain ingredients of animal origin.
Tip:
- If you focus on the European Jewish or Islamic market, familiarise yourself with relevant certification procedures. Many Halal and Kosher certification organisations have advice for suppliers.
Autentika Global carried out this study on behalf of CBI.
Please review our market information disclaimer
Search
Enter search terms to find market research