
8 tips to go green in the cocoa sector
For many years, going green has been a way for exporters to sell to companies and consumers that care about the environment. But going green is becoming more than a way to reach people that want to be more environmentally friendly: it is also becoming a way to do business.
Contents of this page
- Address environmental issues by addressing the root causes
- Stop deforestation through traceability and monitoring
- Reduce your environmental footprint
- Consider carbon finance mechanisms to generate extra income
- Prepare for European laws and regulations
- Incorporate green principles in requirements for your suppliers
- Work with certification and service providers
- Find funding partners and investors
In this study, you can learn about environmental responsibility in the cocoa sector. We explain how threats such as deforestation, climate change and a high carbon footprint can become market opportunities. We also discuss how to comply with laws and regulations and how to meet the demands of your customers. Going green can help you access more markets and contribute to a greener world.
Most sustainability efforts are implemented at the level of cooperatives or farmer groups. If you are a company sourcing from a cooperative, you can work directly with the cooperatives on these tips.
1. Address environmental issues by addressing the root causes
There are many environmental issues in the cocoa sector. In some countries, cocoa production is one of the key reasons forests are disappearing. About 1% of all the forests lost globally between 1998 and 2008 were lost because of cocoa farming. Côte d’Ivoire has lost more than 85% of its forests since 1960, much of it because of cocoa farming. Ghana is losing forests faster than any other country in the world.
Climate change also has an impact on cocoa. Droughts and irregular rain are threatening cocoa harvests. It may no longer be possible to grow cocoa in many parts of West Africa by 2050.
Farmers are using many pesticides. This is bad for the environment and the health of farmers. It impacts biodiversity, which is declining rapidly in many cocoa-producing regions. This threatens cocoa production because cocoa depends on insects for pollination. Higher biodiversity on cocoa farms helps to protect cocoa against drought, pests and disease.
Figure 1: Cocoa production is one of the main causes of deforestation

Source: Mighty Earth
There are many ways in which you can address these environmental issues, which are often caused by farmer poverty. So to address environmental issues it is also necessary to address farmer poverty.
Start with the income of the farmers
Living income is a basic human right. Many cocoa farmers are not earning enough money to make a living. If farmers do not have enough income, this can also lead to many environmental issues. For more details, see Tips to become a socially responsible exporter in the cocoa sector.
Low income leads to environmental issues in different ways:
- Cutting down forests. Many farmers cannot make a living off their land. They need to find more land to grow cocoa or other crops. This can lead to deforestation;
- Using pesticides. Many farmers do not have the money to buy the right pesticides. They also lack the right equipment to protect themselves. As a result, they may use pesticides that are more harmful for the environment;
- Climate change. Adapting to climate change is expensive for farmers. It also costs money to make sure that cocoa doesn’t make climate change worse (mitigation). This article explains different ways in which cocoa farmers can adapt to climate change.
Support farmers
Companies and cooperatives ask farmers to do many things (such as certification, agroforestry, mapping, and applying good agricultural practices). It is important to make sure that farmers know why they are being asked to do this. It will help farmers make the changes that are needed. If farmers don’t know why they have to do something, they probably won’t do it. Farmers need to be seen as partners in addressing environmental issues. Consider setting up meetings or workshops to jointly discuss the importance of these changes. Ask farmers what they think is the best way to take action.
Work with others
Exporters cannot solve farmer poverty on their own. You need to work together with many different stakeholders. These stakeholders can include NGOs, local platforms, governments, service providers and other companies.
In Côte d’Ivoire, one NGO is the Réseau Ivoirien Du Commerce Équitable, which works with cocoa farmers on fair trade and sustainable development. Another NGO is ROSCIDET, committed to the environment and sustainable development. An NGO in Ghana is EcoCare, which works for nature and sustaining livelihoods. The government regulator for cocoa in Côte d’Ivoire is called Le Conseil du Café-Cacao. Cocoa production in Ghana is regulated by Cocobod.
Tips:
- Become a socially responsible exporter (see Tips to become a socially responsible exporter in the cocoa sector for more details);
- Share data and information with farmers;
- Work with civil society, companies, service providers and governments;
- Make sustainability a core part of business decisions.
Set up or join a landscape project
Social and environmental issues such as deforestation, child labour and poverty often apply to entire communities and regions. A solution is to set up a landscape project that goes beyond the cocoa supply chain and covers a geographical area. According to Landscale, a landscape project can range from hundreds to thousands of square kilometres.
A landscape project aims to address the root cause of sustainability issues across whole landscapes or jurisdictions. This means involving other stakeholders and sectors beyond your cocoa supply chain, such as banana, palm oil, vanilla, and even mining.
Landscape projects must involve many stakeholders, including local communities, industry, civil society and governments. They also need companies to work together. Landscape projects are complex to set up, but can also have more impact than supply chain projects.
These are examples of landscape projects:
- ASASE in Ghana. This project works on three levels: farmers, communities and forests. It includes the reforestation of degraded areas and the protection of existing forests;
- Rainforest Alliance in Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire. This landscape project includes tree-planting, setting up landscape management, creating incentives for farmers, and diversification;
- The Kakum Sustainable Landscape Project in Ghana. This is a landscape project in the region that is home to Kakum National Park. One of its goals is the protection of the National Park;
- Swisscontact in Colombia. This project aims to create a sustainable sourcing landscape.
Tips:
- A landscape project can be complex and difficult to set up. To find out more about setting up a landscape project, read the Learning About Cocoa Landscape Approaches: Ghana Guidance Document & Toolbox;
- Learn more about Landscale, which helps with the information in landscape projects;
- Read tip 8 of this report for pointers about finding funding partners and investors.
2. Stop deforestation through traceability and monitoring
Tip 1 explained that deforestation and climate change are among the biggest risks in the cocoa sector. The biggest opportunity to address this is by improving the farmers’ situation. Tip 2 will explain how you can help stop deforestation more directly.
The first step is to improve the traceability of your cocoa. With traceability in place, you can start mapping farms, monitoring deforestation and working in projects that reduce deforestation.
Know where the cocoa comes from (using traceability)
Many EU importers demand to know where the cocoa they buy comes from. This may be because consumers are asking for it, or it may be required by law. Traceability also reduces the risk for companies because they have more certainty about the origin of the cocoa.
Traceability has two main advantages. If you can provide proof of where your cocoa comes from, it can make the cocoa more attractive to your buyers. It is also helpful when addressing environmental risks in cocoa.
Many companies already use systems to trace their cocoa. Companies are also starting to report which cooperatives they buy from. However, a lot of cocoa is still untraceable. Trase, a supply chain transparency initiative, reports that less than half of the cocoa can be traced back to the cooperative. If you don’t know where your cocoa comes from, then you also don’t know whether it came from deforested areas.
You can prove the source of your cocoa in several ways. You can develop your own traceability system or you can use an existing system. Existing systems include the systems of certification programmes such as Rainforest Alliance, Fairtrade and Organic. National traceability systems are also being developed by Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana. When national traceability systems are set up, exporters can also start using those systems for traceability.
There are many levels of traceability in cocoa. They include:
- No traceability;
- Mass balance, which benefits farmers that may or may not be in your supply chain. There is no physical traceability, but you know that farmers somewhere are benefiting from certification. Certification programmes have this option (see tip 7 for details);
- Country-level traceability or Origin Matching Mass Balance, which ensures that if there is demand for certified cocoa from a specific country, the farmers in that country benefit. For more details on traceability to country level, see Origin Matching Mass Balance at Rainforest Alliance;
- Directly working with or supporting cooperatives that you are not buying from physically (dedicated cooperatives without traceability). You know which farmers you are supporting, but you don’t know if you are physically buying their cocoa;
- Traceability in part of your supply chain, for example from farm to cooperative, first point of purchase, exporter, or factory door. Traceability is not in place for your entire supply chain but only for part of it;
- A combination of 3-5;
- Segregated supply chains. This means that the certified cocoa is kept separate from non-certified cocoa in the entire supply chain. This is more difficult to put in place than the levels listed above. One reason is that cocoa is often stored or processed in large quantities. This makes it difficult to keep the cocoa separated throughout the process;
- Mixed Identity Preserved. This means that you know which cooperatives produced the cocoa you are purchasing;
- Identity Preserved. This means that you know which specific cooperative produced the cocoa that you are purchasing. Options 7, 8 and 9 are also offered by certification programmes (see tip 7 for details);
- Full traceability back to farm level.
Tips:
- Determine the level of traceability that you need by asking your customers and by researching market demand. Check whether your customers have traceability commitments, for example to change from an indirect to a direct supply chain. Read tip 5 for more details on traceability levels required by laws and regulations;
- Research whether you can use an existing system or whether you need to develop your own system. Read Tips to become a socially responsible exporter in the cocoa sector for more information about setting up a traceability system for your supply chain.
Track deforestation with remote sensing or farm plotting
When you know the supply chain of your cocoa, the next step is knowing where the cocoa is grown. You can do this with a deforestation monitoring system. Many companies are setting up such systems.
It is also important to know about the different cut-off dates for deforestation. If the land conversion happened after this cut-off date, it counts as deforestation.
Different organisations can set different cut-off dates. This can depend on how strict they want to be or when they made the decision to set a date. For example, the cut-off dates for the Cocoa & Forests Initiative and EUDR are linked to when the initiatives were started. These are the main cut-off dates used for cocoa:
- Rainforest Alliance: January 1, 2014
- Cocoa & Forests Initiative: January 1, 2018
- Fairtrade International: December 31, 2018
- European Union (EU) Regulation on Deforestation-free Products (EUDR): December 31, 2020 The Chocolate Scorecard reports that more and more cocoa companies are using the 2020 cut-off date for their commitments. This is because the EUDR is a mandatory cut-off date. The other cut-off dates are all part of voluntary standards or initiatives.
Tips:
- Join the World Cocoa Foundation and the Cocoa & Forests Initiative (CFI). CFI was set up by companies and the government of Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana to end deforestation and restore forest areas. Joining CFI could help you reach your deforestation goals;
- Monitor deforestation with the right tools. Companies like Satelligence and Farmforce can help with supply chain mapping, traceability and remote monitoring. Rainforest Alliance has a useful platform for remote monitoring. Exporters can also use the Deforestation Risk Analysis tool;
- Determine which cut-off date your customers need for their sustainability goals or compliance with laws and legislation;
- Support farmers with the mapping of farms and by providing them with the right technical tools. Help train farmers on these topics. If you record information about farm size, farm location and cocoa production, make sure that the farmers own this data.
Figure 2: It is important to know where your cocoa comes from

Source: Shutterstock
3. Reduce your environmental footprint
Determine your carbon footprint
Agriculture is a major cause of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. According to the United Nations, Agri-food systems contribute 31% of all GHG emissions, with deforestation as the largest source of these emissions. Cocoa is one of the main drivers of deforestation, and therefore also one of the main causes of GHG emissions. WWF reports that cocoa imports are responsible for more than 11 million tons of CO2-equivalent in the Netherlands.
GHG emissions in the value chain are commonly described as Scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions.
- Scope 1 emissions are ‘direct emissions from owned or controlled sources’;
- Scope 2 emissions are ‘indirect emissions from the generation of purchased energy’;
- Scope 3 emissions are ‘all indirect emissions (not included in scope 2) that occur in the value chain of the reporting company, including both upstream and downstream’.
See the Greenhouse Gas Protocol for more details.
The largest share of the footprint in cocoa is at the cocoa production level, mainly because of land use change. Farm management can also be a large contributor. According to Wageningen University, farm management is a key factor in producing climate-friendly cocoa. The main farm management causes of GHG emissions come from composting cocoa residues and using fertilisers.
The rest of the supply chain also has a carbon footprint. The key parts of the footprint are fermentation, drying, transport, processing, manufacturing and packaging. For cocoa exporters, most of the carbon footprint of cocoa will be outside direct operations (outside scope 1).
Table 1: Main contributors of your carbon footprint in cocoa
| Type | Carbon footprint (CO2-eq) per kg cocoa produced | Scope 1, 2 or 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Land use change (deforestation or degradation) | Land Use Change (LUC) has the largest carbon footprint in the cocoa supply chain. Some examples:
| Scope 3 for exporters and cooperatives. |
| Farm management, including growing, harvesting, fermentation and drying | Farm management can have a positive footprint (net storage) or negative footprint (net emissions), depending on the agricultural practices. For example:
| Scope 3 for exporters and cooperatives. |
| Transport and logistics | It is estimated that transport can account for 9% to 50% of the total footprint depending on farm management. Transportation can cancel out the GHG reductions achieved in organic cocoa production. | Scope 1 or 2 (for own operations) and scope 3 (outside own operations). |
| Factories (processing and packaging) | Processing and packaging are a small part of the overall carbon footprint. However, you can still reduce your overall footprint by making processing and packaging more energy-efficient. | Scope 1 or 2 (for own operations) and scope 3 (outside own operations). |
| Offices and travel | The GHG emissions that result from heating offices and travel are relatively small compared to the other sources of GHG emissions. | Scope 1 or 2. |
Tip:
- Calculate your carbon footprint. There are many sources that can help you estimate your carbon footprint, like Quantis, South Pole, Carbon Roots and Carbon Trust.
Reduce your carbon footprint in cocoa production
The main area to reduce your carbon footprint is by making changes at the farm level.
Agroforestry
One way to reduce your GHG emissions is by helping farmers change to agroforestry. According to Tropenbos, agroforestry has many benefits. It can help mitigate the impact of climate change by storing carbon. It can also help protect cocoa farms from droughts and pests.
It is important that you support farmers if they switch to agroforestry. Farmers need to know why it is important to switch to agroforestry and how they should do this. Farmers also need to be supported financially, since extra investments are needed.
Figure 3: Different ways of growing cocoa, from full-sun to cocoa agroforests
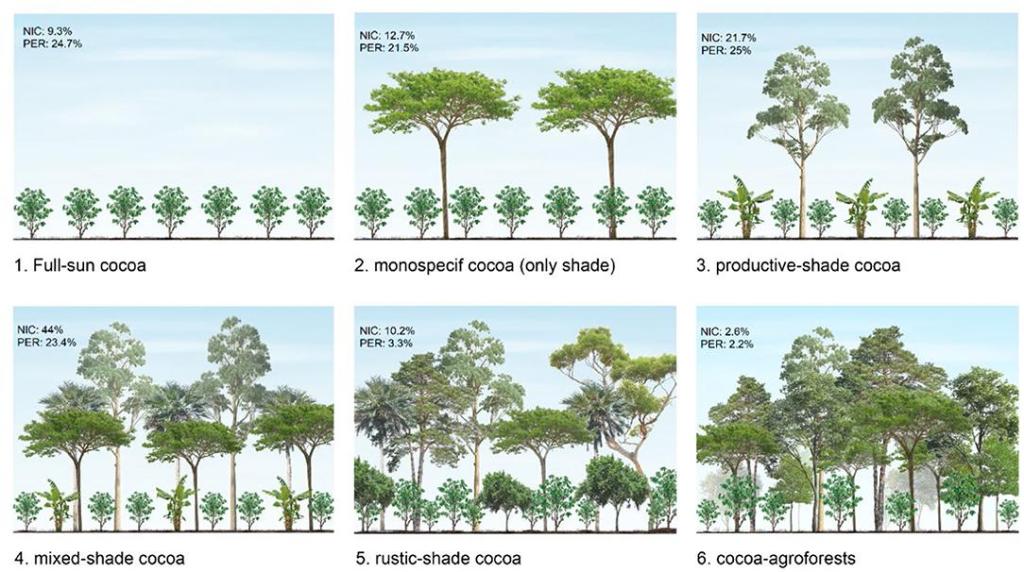
Source: Frontiers
Reforestation
You can also take part in projects to replant forests. Cocoa can become more attractive for importers in the EU if it relates to a reforestation project. There are many EU companies that report on these projects for their supply chains. Such projects include Nestlé’s project to reforest the Cavally forest reserve in Côte d'Ivoire and the World Cocoa Foundation’s reforestation project in Ghana.
Climate-friendly farming
Farmers can change to more climate-friendly farming. A more climate-friendly system causes lower GHG emissions. It will also store a high amount of carbon and produce higher cocoa yields.
One way to do this is with Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA). The objectives of SCA are to increase productivity and income, adapt to climate change and reduce net GHG emissions.
There are also actions that you can take after the harvest. For example, a natural drying process has a lower carbon footprint than gas-dried cocoa.
Tips:
- Read the Tropenbos agroforestry consultation paper for more information on how to implement agroforestry in cocoa. Not all farmers may be ready to implement agroforestry, and you may need different approaches. Check the Smithsonian’s Cocoa Agroforestry Library for more information on agroforestry in cocoa;
- Become involved in a reforestation project. See if it is possible to join an existing project or start a new project. Check with local stakeholders if there are reforestation initiatives in the region where you source cocoa.
Reduce your carbon footprint in the value chain
You can also reduce your carbon footprint in the value chain. This includes transportation, processing and grinding, and packaging.
The main way to reduce the carbon footprint in transport is by making transportation as efficient as possible. For example, exporters can make sure that they use full containers when shipping cocoa. Small specialty cocoa brands can make sure they avoid transporting cocoa by plane, even if it is just a few bags.
The main way to reduce the carbon footprint at factories is by lowering the use of energy and switching to green energy. You can do this by installing solar panels, using wind energy, or using other sources of renewable energy.
You can also reduce your carbon footprint in packaging. For example, manufacturers can reduce or stop plastic use, switch to recycled or FSC certified paper, or use compostable packaging.
Report on your goals and actions
Many European companies and consumers expect companies to report on their carbon footprint. Reporting on your goals and actions can help exporters get better market access in Europe. You can report using the five-step process of the Science Based Target Initiative (SBTi).
- Commit: submit a letter establishing your intent to set a science-based target;
- Develop: work on an emissions-reduction target in line with the SBTi’s criteria;
- Submit: present your target to SBTi for official validation;
- Communicate: announce your target and inform your stakeholders;
- Disclose: report company-wide emissions and track target progress.
Many cocoa companies already use SBTi to set their targets. You can look at the public reports of these companies to learn how to do this. For example, Mars has shared how they set their targets and what they learned from the process. In some cases, reporting is even required by law (see tip 5).
4. Consider carbon finance mechanisms to generate extra income
Another way to generate extra income for cocoa farmers is by setting up a carbon finance project. These projects create carbon credits by reducing GHG emissions. Companies can use these credits to offset their own emissions.
Opinions on carbon credits and carbon finance vary. Some reports show that carbon offsets can contribute to reaching climate targets, others say that carbon credits help companies continue to pollute. Climate-neutral claims among many companies have been increasing in recent years. Be aware that some companies may start to move away from carbon-neutral claims.
This report will focus on the opportunity of carbon finance for farmers and exporters. Carbon finance can be a way to create extra income for farmers. It can also help exporters make their cocoa more attractive to buyers who want to reduce their carbon footprint.
Set up a project
Carbon projects usually need to be quite large. The costs are often too high for smallholder farmers. It can be difficult to set up a carbon project in cocoa. In recent years there have been some new initiatives for smallholder farmers, including the Gold Standard Micro-Scale Programme, Acorn and SarVision.
There are many ways to reduce carbon emissions at cocoa farms, like using cocoa farming as a carbon sink. This means that extra carbon is stored in vegetation (trees), for example in an agroforestry system. This is also called carbon sequestration, as done in the Farmstrong and Acorn project in Côte d’Ivoire.
You can also set up a biochar project. Biochar is created from cocoa husks. By capturing the carbon, you prevent the release of carbon from decomposing cocoa husks into the atmosphere. Biochar can also be used as a fertiliser, as done in the Beyond Beans biochar project.
Tips:
- Talk to your potential buyers in the EU about carbon projects. Is there demand for carbon credits?
- Review the different providers and decide which standard is best for you.
- Work with other stakeholders to set up the project. Stakeholders include cocoa farmers and cooperatives, the companies that buy the cocoa and carbon credits, investors to finance the project, and experts to help set up the project.
Inform and involve farmers
It is important to inform and involve the farmers. The chances of success are higher when the farmers know why they are doing certain things. Project partners should share the money they receive for the carbon credits fairly. This includes all the participating stakeholders, including the farmers.
5. Prepare for European laws and regulations
Becoming a greener cocoa producer or exporter is not only important for the environment or for finding new buyers, it is also becoming a need for doing business in Europe. There are many laws and regulations that you need to comply with when exporting cocoa to Europe, and many voluntary requirements that are seen as a minimum for doing business.
EU Green Deal
The European Commission (EC) launched the European Green Deal (EGD) in 2019. The EGD aims to make the EU climate-neutral by 2050. This is a binding commitment under the EU Climate Law.
To get there, EU members commit to reducing net greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030. The EU has also committed to planting an extra 3 billion trees by 2030.
The EU has launched several initiatives to reach these goals. These include clean transport, green energy, restoring nature, funding climate action, and many other initiatives. See the article The EU Green Deal – How will it impact my business? for more details. The initiatives that are most relevant for cocoa will be described here.
Prepare for regulation on deforestation-free products by December 2025
The EU wants to minimise the contribution to deforestation and forest degradation worldwide. The EU has therefore proposed a regulation to curb EU-driven deforestation and forest degradation. This is the EU Regulation on Deforestation-free Products (EUDR). All cocoa products that you export to the EU will need to comply with this regulation. The EUDR is a key regulation under the broader EU Green Deal.
The new regulation entered into force on June 30, 2023. The EUDR was set to start per December 30, 2024, but the start has been delayed by 12 months. Companies must now comply with the new rules by December 30, 2025. Micro and small enterprises (MSEs) will have an extra six months to comply, which means they would need to be compliant by June 2026.
Here is a brief description of the key elements:
- Due diligence statement. Companies are only allowed to import cocoa that is both deforestation-free and legal. You need to cover all cocoa imports with a due diligence statement;
- Traceability. The regulation requires traceability of the cocoa to the plot of land where it was produced;
- Deforestation cut-off date. Cocoa from land that was deforested or degraded after December 31, 2020 cannot be sold in the EU;
- Geolocations. All cocoa plots must be polygon mapped (for plots larger than 4 hectares) or GPS mapped (for plots smaller than 4 hectares);
- Benchmarking system. There will be a benchmarking system that assigns risks to countries and regions. The risk level determines what you need to do. This benchmarking system is scheduled to be published in 2025;
- Agroforestry is not an alternative. Agroforestry cocoa produced on land that was deforested after December 31, 2020 will not be accepted in the EU market.
For more information about the EUDR, see our study Tips to become EUDR-compliant in cocoa.
Tips:
- Make sure that you comply with the regulation on deforestation-free products. Visit the EU website for the most recent information;
- Support farmers to make sure they comply. Farmers and cooperatives need to make many investments to have mapping and traceability in place. Provide training and finances, and work with other stakeholders.
EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive
The EU also has other laws and regulations that could be relevant. You may also need to comply with the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), which encourages accountability and transparency. Companies must provide information on social and environmental risks and on the impact of their activities on people and the environment. Companies that fail to comply with the CSRD can receive financial penalties.
The CSRD will be mandatory for all companies with over 250 employees and over €40 million in annual turnover. This will start in 2024, 2025 or 2026, depending on a few factors. The first group that needs to report are large, listed companies. They need to report on the 2024 financial year for reports published in 2025. See the EU website for details.
Some exporters may need to comply with the CSRD. This is the case if:
- You generate a net turnover of over €150 million in the EU, and;
- You have at least one subsidiary or branch in the EU.
You may also get information requests from your buyers if they fall under the CSRD.
In 2025 there are discussions to consolidate the CSRD with the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) and EU taxonomy. In February 2025, the EC proposed an “Omnibus approach”. If it is accepted, it would reduce the number of companies that need to report by 80%. It would also limit the data collection and reporting that companies would need to do.
Next, the European Parliament (EP) and European Council will review the proposal. This can take up to 18 months, but they will try to speed up this process. The EP and Council can also add more changes to the proposal before it is accepted. The current requirements apply until the proposal is accepted. See our study on How to become more socially responsible in cocoa for more information about CSDDD and the Omnibus proposal.
6. Incorporate green principles in requirements for your suppliers
Aligning with the requirements of your buyers can make it easier for you to become more environmentally friendly. Many cocoa companies publish the requirements in a Supplier Code of Conduct. These requirements often include both social and environmental requirements. For more details on social requirements, see Tips to become a socially responsible exporter in the cocoa sector.
Learn about Supplier Codes of Conduct
Supplier Codes of Conduct can contain many elements. These are often about social topics, but sometimes also include environmental requirements. See the table below for examples.
Table 2: Examples of environmental requirements in a Supplier Code of Conduct
| Supplier Code of Conduct |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Publish a Supplier Code of Conduct for your suppliers
You can also set up your own Supplier Code of Conduct to make sure that your suppliers are more environmentally friendly.
In a Supplier Code of Conduct it is important to consider how far up the supply chain it applies. It can apply only to your direct (tier 1) suppliers, or further up the supply chain to the suppliers of your suppliers (tier 2). You can increase your impact by increasing how far the Supplier Code of Conduct applies.
A Supplier Code of Conduct can also have requirements for suppliers that are not cocoa producers or cooperatives, such as:
- Suppliers need to have a Supplier Code of Conduct or environmental policies;
- Suppliers need to have targets and action plans for reducing the impact on the environment;
- Suppliers need to report on their greenhouse gas emissions, also in their supply chain (scope 2 and 3).
Tips:
- Read the Supplier Codes of Conduct of your potential buyers and other chocolate companies, for example the Tony’s Chocolonely 5 Sourcing Principles, the Mars Supplier Code of Conduct, the Hershey Supplier Code of Conduct, the Cargill Supplier Code of Conduct and the Ecom Supplier Code of Conduct;
- Make sure that you comply with the requirements in the Supplier Code of Conduct of potential buyers.
7. Work with certification and service providers
When going green in cocoa, there are programmes and services that can help you with practical guidance and support. There are many programmes and services in the cocoa sector. These include certification programmes such as Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance and Organic. There are also many platforms and initiatives.
Learn about the phases of sustainability
To determine where to find the right support, it is helpful to first describe where cocoa is in the transition to sustainability. New Foresight describes four phases in the transition to sustainability.
- Inception. This is when people start to be aware about the sustainability issues in the sector;
- First Movers. Some companies start to take action and use sustainability as a competitive advantage;
- Critical Mass. Most companies are taking action. Multi-stakeholder initiatives are set up with industry, civil society, governments and academia;
- Institutionalisation. There is a level playing field. Sustainability is the ‘new normal’.
Figure 4: The four phases in the transition to sustainability
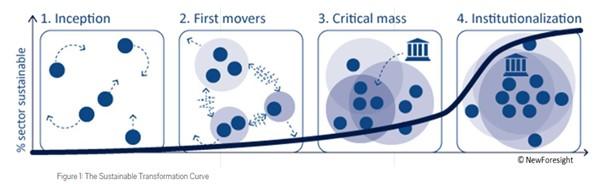
Source: New Foresight
The cocoa sector is now starting phase 4 of this model. There are already many multi-stakeholder initiatives. These include the Cocoa & Forests Initiative, the Initiatives on Sustainable Cocoa and the International Cocoa Initiative. In tip 5 we described how laws and regulations are implemented to create this level playing field. These are included in the multi-stakeholder dialogue for sustainable cocoa.
You can work with a certification or sustainability programme to help you reach your environmental goals. Below we describe the main Voluntary Standard Systems in cocoa and how they can help you.
Work with Rainforest Alliance and Fairtrade
Certification can help you become more environmentally friendly. The largest certification programmes available in cocoa are Rainforest Alliance and Fairtrade. Study both programmes to determine which one works best for you.
A factor that can determine your choice is the available traceability levels. It is essential to know where your cocoa comes from when you want to address sustainability risks in your supply chain. The level to which you can trace cocoa varies per standard. The main traceability levels are Mass Balance, Segregated and Identity Preserved. For more details, see the explanations from Fairtrade and Rainforest Alliance.
Another factor that can determine your choice is the mapping and deforestation monitoring of the programmes. Both programmes already have mapping requirements. Rainforest Alliance has aligned their standard with EUDR requirements. Farm Certificate Holders can choose self-selected criteria to help them comply with the regulation. Rainforest Alliance also offers a Deforestation Risk Assessment Tool.
Fairtrade also supports producers and exporters with EUDR compliance. Fairtrade works with Satelligence to help farmers map their plots and get deforestation risk information.
Tips:
- Read Entering the European market for certified cocoa. For more details on certifications, see Tips to become a socially responsible exporter in the cocoa sector;
- Choose the right traceability level. If the cocoa is traceable, it could help you with EU regulations;
- Use the Fairtrade Risk Map or the ISEAL Deforestation Risk Analysis to see how much risk there is.
Work with organic-certified cocoa
Selling organic-certified cocoa can help you get access to new buyers. CBI reports that demand for organic cocoa in the EU continues to grow.
Organic certification is regulated centrally by the EU. The EU has strict control and enforcement on organic products. Imported organic cocoa must conform to equivalent standards as the EU standard. Importers have to follow procedures if they want to sell the cocoa as organic.
If you want to export to countries outside of the EU, check the required legislation for that country. Examples are the Swiss Organic Law in Switzerland and the Organic Products Regulations in the United Kingdom.
Complying with organic criteria can be quite demanding. You can only sell a product as organic if all the ingredients are organic-certified. This is not always possible when a product has too many different ingredients. Some companies will still buy organic cocoa even if the company will not sell the final product as organic.
The use of pesticides in other crops is a major threat to organic cocoa. There is a higher risk of pesticides leaking to cocoa production from other crops that are not organic (for example rice or bananas). In some areas it is even becoming too difficult to sell organic because of the contamination. Some regions cannot produce enough organic cocoa to meet demand. This risk is especially high in Latin America.
If you want organic certification, it is important to discuss with farmers why it can help to grow organic cocoa. Farmers also need technical support to help them grow organic cocoa. You can help farmers make sure that they meet organic standards.
Tips:
- Read Entering the European market for organic cocoa for more information on organic cocoa;
- Help farmers grow organic cocoa. Explain what organic means and make sure that farmers receive the right training;
- Think about combining organic certification with another certification programme (for example Rainforest Alliance or Fairtrade). This can make the cocoa more attractive for some buyers.
Africa Regional Standard (ARS)
There are also other standards for cocoa production. One of these is the Africa Regional Standard (ARS) developed by Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana. The ARS was finalised in 2021. National implementation guides are available for Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire. The ambition is to make this standard mandatory for all cocoa farmers in those two countries.
It is important to note that if the cocoa is compliant with the ARS, it does not automatically mean that it complies with the EU due diligence requirements. Read this paper for details.
Tip:
- Watch the development of the Africa Regional Standard. Ensure that you are compliant if the standard becomes mandatory.
Company programmes
Many companies have their own sustainability programmes that claim to make cocoa more sustainable and environmentally friendly. However, in many cases these programmes are not independently verified. This means that they are not checked by independent third-party organisations. Also, many programmes do not publish a Standard. It is therefore difficult to compare the quality of these company programmes.
Tip:
- If you decide to work with a company sustainability programme, ask the company for independent proof of the impact of the programme. Review their standards and requirements and decide whether complying with them can be beneficial.
8. Find funding partners and investors
Many of the tips described above are costly. It is helpful to find funding partners and investors to finance going green in cocoa. Environmental plans can also make you more attractive for funding partners and investors.
Working with funding partners and investors can make your cocoa more attractive for buyers as well. This is because buyers know that you have external financial support for your projects and initiatives.
There are many funding partners and investors that can help you. These include:
- GIZ. See the project data page for details on current and new projects;
- The Initiative for Sustainable Trade (IDH). Check their website for new Calls for Proposals;
- USAID. See Funding Opportunities for details;
- Swisscontact can be a partner with their development programme;
- World Bank. See Procurement Framework and Regulations for Projects for details;
- United Nations Development Programme. See Procurement Notices for details;
- Rainforest Alliance (for example through the Africa Cocoa Fund) and Fairtrade;
- The Swiss Initiative for Sustainable Cocoa (SWISSCO) made funding available for cocoa landscape projects in 2023. Beyond Chocolate also made funding available for nine projects.
Tips:
- Research current funding opportunities. Funding may already be available for the projects that you want to implement;
- Propose your projects to funding partners and investors. Work with other stakeholders to create a stronger proposal;
- Research similar projects to see which funding partners and investors are involved. Contact these funding partners and investors to ask if they are interested in funding a similar project.
Molgo Research carried out this study in partnership with Long Run Sustainability and Ethos Agriculture on behalf of CBI.
Please review our market information disclaimer.
Search
Enter search terms to find market research

